Introduction
Overview of Product Management
Product management is an essential organizational function that centers on the product and its customers throughout its lifecycle. This includes everything from development to positioning and pricing. The product manager advocates for customers within the organization and ensures that the market’s voice is heard and heeded to determine the product’s success and develop the best possible outcome. Successful product managers work closely with various teams and departments to accomplish their goals and showcase their leadership skills.
- Research is crucial if a product manager wants to gain expertise about the company’s market, user personas, and competitors, which are fundamental to shaping business strategy and product ideas. This knowledge is then transformed into a high-level strategic plan encompassing goals, objectives, an overview of the product, and a rough timeline.
- Effective communication is paramount in product management. A successful product manager develops a strategic plan using a product roadmap and presents it to key stakeholders, including executives, investors, sales team, marketing team, and development teams, to ensure alignment and support for the product’s vision. Product managers communicate with cross-functional teams throughout the development process, ensuring customer satisfaction remains a top priority.
- Once the strategic plan receives approval, product managers coordinate with relevant teams, such as product marketing and development, to execute the plan, thus demonstrating their project management skills. They are crucial in coordinating the development process, ensuring the product aligns with the strategic vision and that customer satisfaction is achieved.
- Feedback and data analysis play a significant role in product management. After the product is built, tested, and introduced to the market, product managers gather data and solicit direct feedback from users. This is one of the analytical skills that help them understand what aspects work, what don’t, and what improvements can be made, allowing them to make data-driven decisions and enhance customer satisfaction. They collaborate with relevant teams to incorporate this feedback into future product iterations, ensuring continuous improvement.
- In the tech industry, where innovation is rapid, gaining a deep understanding of customers and designing customized solutions is crucial for success. Product management is a strategic function where product managers establish the overall purpose of a product, aligning it with business strategy to ensure its success in the market. They inform the rest of the company about product goals and aims, ensuring everyone adopts a common strategy and remains customer-centric.
To streamline operations, tactical tasks such as scheduling and workload management are often delegated to project managers, allowing them to focus on higher-level planning and strategic decision-making. This separation of roles ensures that product managers can dedicate their time and expertise to shaping the product’s direction and driving its success.
Importance of Product Management Skills
Role of Artificial Intelligence in Product Management
In modern product management, the importance of artificial intelligence cannot be overstated. AI is pivotal in efficiently obtaining, digesting, and analyzing vast amounts of data, enabling product managers to make well-informed decisions and enhance their strategic planning. I think if a product manager doesn’t embed artificial intelligence into its operations, many opportunities are missed.
AI-powered tools and algorithms assist product managers and their engineering teams in conducting extensive research and collecting data (a good example is https://collato.com).
These technologies can crawl through various data sources, including market trends, customer behavior, social media, and competitor insights, to comprehensively understand the industry landscape. By leveraging AI, the product manager and her engineering teams can swiftly identify emerging trends, user preferences, potential opportunities, and their own pain points, which are invaluable for creating customer-centric products.
Moreover, AI helps in processing and analyzing complex datasets quickly and accurately. Traditional data analysis methods may be time-consuming and are limited in scope. Still, AI algorithms can sift through vast volumes of data, identifying patterns and correlations that human analysts might overlook. This enables product managers and their engineering teams to gain deep insights into customer preferences and behaviors, allowing them to tailor product features and functionalities precisely to meet their customers’ needs.
That will automatically help product managers revisit the product vision and discuss it with the marketing team, teams with technical skills, those who create technical product specs, and executives. Discussing the product vision is a critical part of risk management. If the product manager uses strategic thinking to analyze data fast, build AI-powered predictions, and implement continuous learning, many risk factors can be eliminated and mitigated. It will eventually help shorten the market time and make a successful product launch a reality.
One of the most significant advantages of AI in product management lies in its predictive capabilities. AI-powered predictive analytics can forecast future market trends, customer demands, and potential risks. By building predictive models, product managers and their engineering teams can anticipate market shifts and identify opportunities for innovation and growth. Prediction can influence customer conversion rate positively as product managers can design actions that mitigate churn and control key performance indicators. This foresight is vital for staying ahead of the competition and informing product strategy to position products strategically in the market.
AI also plays a critical role in personalizing product experiences by conducting market research. With AI-driven recommendation systems and user profiling, product managers and their engineering teams can offer customized product suggestions to individual customers, enhancing user engagement and satisfaction. Personalization improves customer retention and helps create a loyal customer base, driving revenue and success for the product.
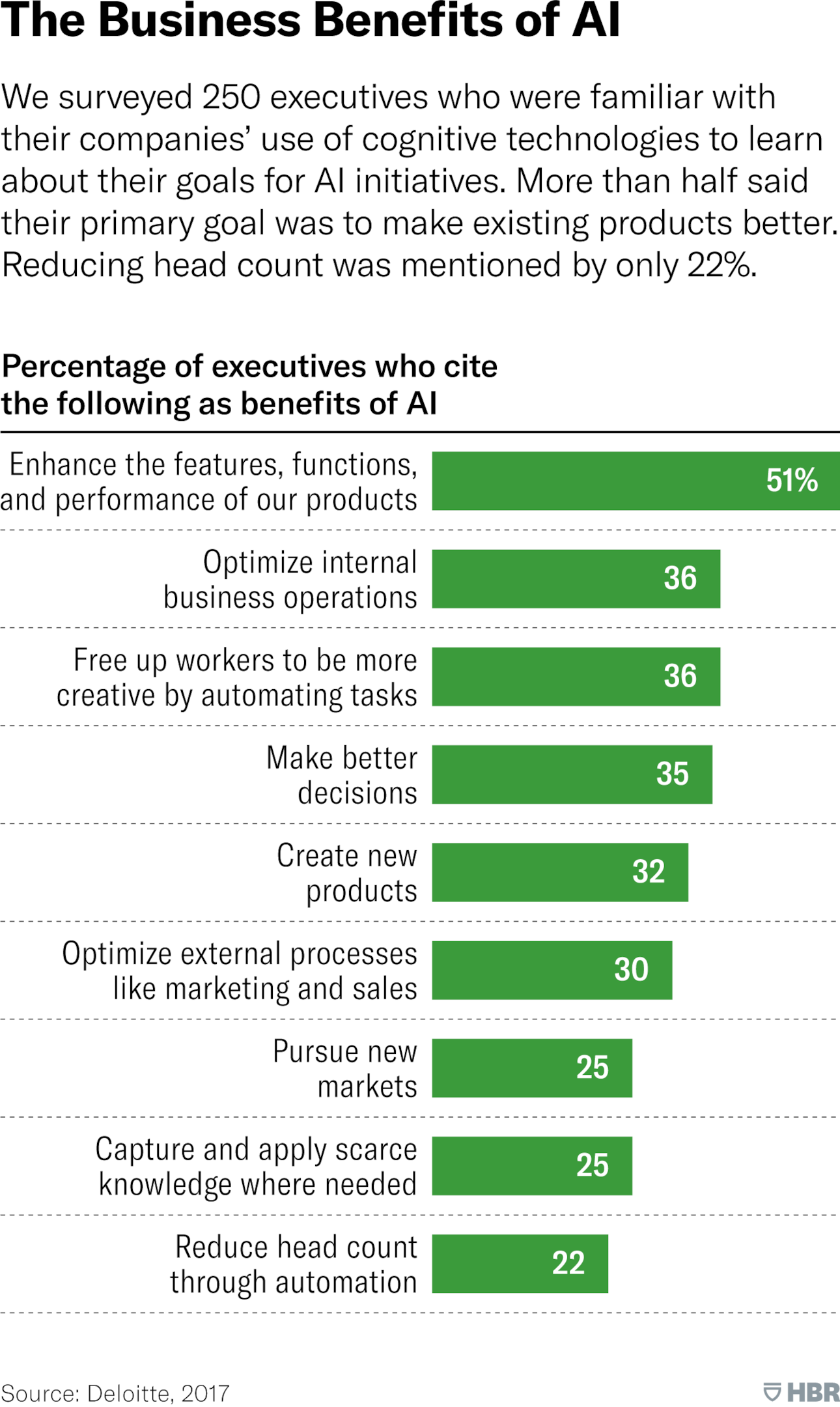
An interesting survey, which I believe can help every product manager, was conducted among 250 executives well-acquainted with their companies’ utilization of cognitive technologies to understand their objectives regarding AI initiatives. Over 50% of the respondents indicated that their primary focus was to enhance the quality of their current products (Source: Harvard Business Review, https://hbr.org/2018/01/artificial-intelligence-for-the-real-world). I perceive it as a tremendous opportunity for product managers to combine their soft skills, analytical skills, and communication skills with hard skills such as roadmap planning, execution, and relationship management. This synergy of product manager skills can significantly benefit the business.
Furthermore, AI enables product managers and their engineering teams to automate product development and management processes. Using machine learning algorithms, product managers and their engineering teams can automate tasks like A/B testing, feature prioritization, and user segmentation, saving time and resources while maintaining precision and accuracy. Strong prioritization skills are essential for product managers to ensure that the engineering team focuses on the most valuable features and tasks.
Artificial intelligence also works as an “active listening tool.” It’s interesting that through listening to data from many different points, AI can help determine success by suggesting changes to a new product development process. Without a doubt, understanding ways to incorporate AI for the betterment of the company is a sign of a successful product manager and an indicator of a product manager’s ability.
Important Skills for Successful Product Managers
Understanding the Role of a Product Manager
Product managers are the unsung heroes of successful product launches. They are critical in helping organizations bring products to market and increase revenue. A successful PM is strategic, detail-oriented, and customer-focused. They understand the customer’s needs and collaborate with stakeholders to develop effective product roadmaps.
A PM’s breadth of important skills is unmatched, ranging from technical management to communication and analytical thinking. Ultimately, the role of a successful PM entails bridging the gap between a product’s development and market success. It’s a challenging role that requires a proactive approach, an unwavering commitment to excellence, and leadership skills. Aspiring product managers must deeply understand their role’s significance and remain focused and inspired while working towards achieving their team’s goals.
Based on my experience and projects, I defined the most critical areas where product manager skills are irreplaceable. I also want to say that those responsibilities require solid product management skills; without them, product failure is inevitable. Here they are
- As a product manager, it is essential to regularly conduct market research to understand customer needs better, identify market trends, and gather insights that will inform product decisions. This can include analyzing customer feedback surveys, conducting competitor analysis, and keeping an eye on industry reports to stay up-to-date on market dynamics.
- As a product manager, it’s crucial to establish a product strategy that aligns with the broader business objectives. This includes determining the product vision, identifying target markets, and outlining essential product features. A roadmap may be created to prioritize specific characteristics based on market demand and business goals.
- Collaborate with Cross-Functional Teams: Product managers must collaborate closely with various teams, such as engineering, design, and marketing, to ensure smooth product development and launch. They should facilitate effective communication, coordinate tasks, and resolve conflicts or challenges.
- Maintaining a well-managed product backlog is crucial for effective product management. Prioritizing features, user stories, and tasks can be challenging, as it requires balancing competing demands. Customer value, technical feasibility, and business impact are essential when prioritizing backlog items. User story mapping or impact-effort matrix techniques are helpful tools that can be used to prioritize backlog items effectively.
- Measure and Analyze Product Performance: Evaluating the success of a product is essential, and product managers should define relevant metrics and track them over time. They must analyze data, gather user feedback, and use insights to drive iterative improvements. For example, they may measure key performance indicators (KPIs) like user engagement, conversion rates, or customer satisfaction scores to assess the product’s performance and inform future iterations.
Technical Expertise That Product Managers Need
Product managers are vital in leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) within organizations. According to the data provided, 21% of AI users are product managers, highlighting their recognition of AI’s value. Product managers harness AI capabilities to enhance product development, improve customer experiences, and drive product roadmap in the right direction. Basic knowledge is not enough, though. Strategic thinking and analytical skills must go hand in hand with understanding the potential of cloud, artificial intelligence, and data analytics.
The Importance of Technical Knowledge in Product Management
Not only can new product development processes be enhanced by artificial intelligence, but, as Harvard Business Review research mentioned above, current products can be empowered by machine learning and deep learning.
As emphasized in the previous section, technical expertise is essential for product managers to collaborate with cross-functional teams and make informed decisions effectively. Possessing technical knowledge is one of the hard skills that establish credibility among teams and stakeholders, facilitating smoother communication with developers and engineers. It allows product managers to speak the same language as their technical team, leading to better problem-solving and fostering trust and respect.

Technical knowledge empowers product managers to lead cross-functional teams more effectively by enabling a comprehensive understanding of the technical obstacles faced by the team. By anticipating potential problems and proactively finding solutions, product managers facilitate increased efficiency within the team, minimizing the risk of delays and issues during product development. Effective communication with team members is also enhanced, resulting in a more cohesive and collaborative environment.
Furthermore, technical knowledge enhances the ability of product managers to communicate effectively with their teams and stakeholders. They can proficiently explain technical concepts (frameworks, diagram flows, technology abilities) and requirements, leading to more productive collaboration and superior solutions. Enhanced communication capabilities facilitate more robust relationships with the team and stakeholders, driving the project’s overall success.
Technical knowledge also expands the scope of work that product managers can handle. Understanding the technical aspects of the product enables a better assessment of the feasibility of new features and product ideas. This aptitude for evaluation helps identify opportunities to enhance the product’s capabilities and explore new markets, driving increased revenue and business growth.
Additionally, technical knowledge enhances problem-solving skills which is a large part of the many essential product manager skills a PM should have. Product managers are entrusted with solving complex problems that arise during product development, and technical knowledge equips them with the technical skills to analyze and resolve these problems more effectively. It enables a deeper comprehension of the root causes of problems, leading to more effective and sustainable solutions, thus mitigating the risk of future issues.
While there are differing viewpoints on whether product managers need a technical background, having technical skills provides several advantages. It allows for stronger working relationships with software engineers, a better understanding of technical limitations, and the ability to plan product roadmaps effectively. However, even without a technical background, product managers can still learn essential technical aspects on the job and collaborate effectively with their teams.
Distinguishing Factors For Internal and External Stakeholders in Interactions with a Technically Skilled Product Manager
This, made up by my story, is a good example of why stakeholders, markets, and teams appreciate product managers with more than soft skills. Let’s have a look.
Let’s say the product manager, Nora, works for a medical company specializing in developing therapies. Nora has a solid technical background and an in-depth knowledge of mobile app development, including programming languages, frameworks, and operating systems like iOS and Android.
One day, Nora’s team proposes a new feature idea for their flagship medical tracking app: integrating advanced facial recognition technology for personalized user experiences. With her technical expertise and hard skills, Nora evaluates the feasibility of this feature by considering specific technologies and factors.
The real difference doesn’t mean only communication skills
She delves into facial recognition algorithms’ technical requirements and limitations, such as OpenCV for computer vision processing and deep learning frameworks like TensorFlow or PyTorch for facial recognition models. Nora also assesses the performance impact of implementing these technologies on various mobile devices, ensuring a smooth user experience across a wide range of hardware.
After a comprehensive analysis, Nora determines that integrating facial recognition technology is technically viable within the company’s resources and can provide substantial benefits. She recognizes that this feature has the potential to enhance the app’s user engagement, improve security measures, and attract users who value personalized experiences.
Nora presents her findings to the senior management, emphasizing the advantages of leveraging specific technologies like OpenCV and deep learning frameworks for facial recognition. She explains how this feature can open up opportunities in industries such as e-commerce, where personalized recommendations can drive conversions, and security applications, where biometric authentication is crucial.
In this fine example, Noras’s technical knowledge of specific technologies like OpenCV, TensorFlow, and PyTorch enables her to assess the feasibility of the facial recognition feature. Understanding these technical aspects allows her to make informed decisions and effectively communicate the potential benefits, contributing directly to increased revenue and business growth.
Data Skills in Product Management
Product managers need data and analytical skills for three key reasons:
- To make data-driven decisions based on customer behavior, market trends, and product performance.
- To better understand their customers and create personalized experiences.
- To measure and optimize product performance through tracking key metrics and conducting A/B tests.
Leveraging Data Skills for Effective AI-Powered Products
Understanding artificial intelligence, namely, machine learning (ML) and different algorithms, is crucial for a product manager who works with data and artificial intelligence-powered products.
AI and ML technologies are transforming various aspects of product management, including user personalization, predictive analytics, recommendation systems, and process automation. Not only should the engineering team be aware of that. By understanding the fundamental concepts of AI and ML, product managers can effectively leverage these technologies in their product development process and identify opportunities where they can add value and increase the chances of product success.
A key aspect of understanding AI and ML is algorithm selection. Different algorithms serve different purposes and have varying strengths and limitations (supervised, unsupervised, filtering, Bayesian, etc.). Product managers must know various ML algorithms to select the most appropriate one for a specific use case.
When creating a model, it’s essential to consider multiple factors such as the type of data, the level of complexity in the model, how easy it is to interpret, what it takes to re-train the mode, how long it takes to train it, and whether or not it can scale effectively. Understanding those algorithms and models helps to make informed decisions and decide, for instance, which solution will consume less energy and be more nature friendly. Market research skills are not enough here. Experimenting with algorithms is a game changer.
Furthermore, product managers need to evaluate the performance of ML models to ensure they meet the desired objectives. Understanding evaluation metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, or area under the curve (AUC) helps product managers assess the effectiveness of AI and ML solutions and make informed decisions regarding their deployment.
Ethical considerations are another important aspect of AI and ML. These technologies raise concerns about bias, fairness, privacy, and transparency. A product manager should know these considerations to ensure AI-powered products are developed and deployed ethically and responsibly. This involves understanding the potential biases in data, algorithmic decision-making, and mitigating the impact of discrimination on user experiences. Ethics is significant for a product and brand reputation and can shape a successful career.
Effective collaboration with data scientists and engineers is vital for product managers. Understanding AI and ML concepts helps product managers communicate and collaborate effectively with technical teams (do you know what a model parameter is, what is the difference between a parameter and a data point?), aligning product requirements with technical feasibility, and understanding the implications of various algorithmic choices.
Lastly, product managers need to be able to stay updated on the latest AI and ML trends, advancements, and best practices. AI and ML technologies are evolving rapidly, and product managers must adapt to this changing landscape. This includes understanding new algorithms, emerging techniques, and AI and ML industry-specific applications. A fantastic example is the evolution of GPT, which started from text and now can efficiently process graphics, tables, and plugins. A product manager who doesn’t follow this might develop products that, when launched, will be obsolete from day one.
The technical expertise product managers have can harness the power of these technologies, make informed decisions, drive innovation, and create products that deliver value to users and businesses. It enables them to leverage data effectively, develop AI-driven strategies, and navigate the evolving landscape of technology and consumer expectations.
The Intersection of AI and Product Management and Why Data Monetization Should be The Primary Concern of The Product Team
The intersection of AI and product management has brought about transformative changes in how companies develop and market their products. As AI technologies continue to evolve and advance, product managers need to adapt their strategies to leverage the power of AI for data monetization. In today’s data-driven world, data monetization should be the primary concern of the product team, as it offers immense opportunities for revenue generation and business growth.
AI’s Impact on Product Management
Product managers can gain valuable insights into customer behavior, market trends, and competitive landscapes with AI-powered tools and techniques. This information enables them to make informed decisions and develop effective product strategies. AI solutions based on natural language processing or other methods can analyze vast amounts of data and provide actionable recommendations, allowing product managers to refine their offerings based on customer preferences and market demands.
One crucial skill for product managers in the AI era is critical thinking. With abundant data at their disposal, product managers must be able to identify relevant information, filter out noise, and make informed decisions. They need to be able to analyze data and extract actionable insights to drive the company’s vision and product strategy. This requires a deep understanding of the underlying AI technologies and the ability to interpret the results generated by AI-powered tools.
Leveraging AI for Data Monetization of Products
Data monetization emerges as a crucial skill for product managers. Companies can unlock the value of their data by leveraging AI to create new revenue streams. Data monetization involves transforming raw data into valuable products or services customers are willing to pay for. For example, a product manager in the e-commerce industry can analyze customer browsing and purchasing patterns using AI tools, such as recommendation systems, to offer personalized product recommendations or targeted advertisements. Here is a list of products I have found helpful in the intersection of product management and artificial intelligence:
- MonkeyLearn (https://monkeylearn.com/) offers a suite of AI-powered text analysis tools. With their platform, product managers can extract insightful information from vast text data, including customer reviews, social media posts, and survey responses. The tools provided by MonkeyLearn assist product managers in comprehending customer sentiment, pinpointing crucial topics, and using data to refine their product offerings through informed decision-making.
- Clarabridge (https://www.clarabridge.com/) is a customer experience management platform that utilizes natural language processing and sentiment analysis to analyze customer feedback from various sources. Clarabridge is a valuable tool for product managers to gain insight into customer preferences and identify emerging trends. This information allows them to make data-backed decisions to enhance their products based on customer demands.
- RapidMiner (https://rapidminer.com/) is a data science platform offering various AI and machine learning tools for data analysis and predictive modeling. You can benefit from RapidMiner’s text analytics capabilities as a product manager. This tool allows you to efficiently process large text datasets and uncover patterns to generate insightful data. This way, you can understand your customers’ preferences and optimize your product offerings to meet their needs.
- H2O.ai (https://www.h2o.ai/) provides an open-source platform for AI and machine learning. Their tools include natural language processing capabilities that help product managers analyze unstructured text data. By leveraging H2O.ai, product managers can gain insights into customer feedback, sentiment, and preferences to inform product development and strategy.
- Aylien: Aylien (https://aylien.com/) offers a range of AI-powered text analysis APIs and solutions. Their tools utilize natural language processing to extract structured data from text documents, classify content, perform sentiment analysis, and summarize information. Product managers can leverage Aylien’s tools to analyze customer feedback, understand market trends, and make informed decisions to improve their products.
A product manager needs to implement AI-powered data monetization strategies to achieve data monetization successfully. This involves identifying the data assets within the company, determining their value, and developing innovative ways to monetize them. AI tools can assist this process by providing predictive analytics, customer segmentation, and pricing optimization. For instance, product managers can utilize AI-powered pricing optimization tools like PROS (https://www.pros.com/) or Zilliant (https://www.zilliant.com/) to determine optimal pricing strategies based on market dynamics and customer preferences.
By harnessing the power of AI to analyze and interpret data, product managers can make informed decisions, refine product strategies, and align with the company’s vision. As AI advances, product managers must stay updated on the latest AI technologies and tools to capitalize on data monetization benefits effectively. Understanding these technologies has become one of the basic product management skills a PM should have.
Developing a Product Roadmap with AI
Overview of Product Roadmaps
A product roadmap is a strategic blueprint that outlines a product’s vision, goals, and direction over a specific time frame. It is a guiding document for product development teams, stakeholders, and executives to understand the product’s evolution and align their efforts with the overall business strategy.
Traditionally, product roadmaps have been created through market research, customer feedback, and team collaboration. However, with the rise of Artificial Intelligence, integrating AI in product roadmap planning has become increasingly prevalent, providing organizations with a competitive edge and fostering innovation. But the question is, how to find opportunities for AI to serve the product and customers? Let’s have a look at a couple of strategies and examples.
Integrating AI in Product Roadmap Planning
Integrating AI in product roadmap planning opens up a new realm of possibilities, as it empowers businesses to harness the potential of machine learning, natural language processing, and other AI technologies to enhance decision-making, automate processes, and gain valuable insights from data.
AI is primarily known for its predictive capabilities, allowing businesses to anticipate customer behavior, market trends, and product demand, which significantly impacts the success of a product.
It’s essential to remember that automation only sometimes requires AI. Numerous robotic process automation (RPA) implementations have incorporated automation without AI. However, predictive capabilities are not possible without AI.
Predictive Analytics in Customer Behavior
AI can be harnessed to predict customer behavior and preferences, enabling businesses to effectively tailor their products to meet customer needs. For instance, an e-commerce platform can use AI algorithms to analyze previous customer interactions, browsing habits, and purchase history to forecast what products a customer might be interested in buying next. This predictive approach provides extensive market research, which helps deliver personalized product recommendations that increase conversions and customer satisfaction.
Anticipating Market Trends
AI-driven predictive analytics can help businesses anticipate market trends and adjust their product roadmap. Organizations can identify emerging trends and respond proactively by analyzing market data, social media trends, and consumer sentiment. For example, a fashion retailer can leverage AI to monitor fashion influencers and social media conversations, allowing them to predict popular styles and adapt their product offerings in real-time, thus staying ahead of competitors.
Forecasting Product Demand
Accurate demand forecasting is crucial for inventory management and meeting customer expectations. AI-powered forecasting models can analyze historical sales data, seasonal patterns, and other relevant variables to predict future product demand. This helps businesses optimize inventory levels, minimize stockouts, and reduce excess inventory costs. For example, a grocery store chain can use AI to predict the demand for specific items during different seasons, allowing them to ensure they have sufficient stock on hand to meet customer needs even in a niche customer market.
Churn Prediction for Customer Retention
AI’s predictive capabilities can also predict customer churn, which is critical for businesses relying on subscription-based models. By analyzing customer behavior and engagement patterns, AI can identify potential churners and provide insights into why customers might be at risk of canceling their subscriptions. This enables businesses to proactively retain customers by offering personalized incentives or improving customer support. For example, a video streaming service can predict which users will likely churn and offer exclusive content or discounted subscription plans to encourage retention.
Conclusion
Recap of Key Points
To summarize, product managers must understand the potential of AI and how it can be used to improve product planning and the product life cycle in many different ways. By leveraging predictive analytics and market intelligence, organizations can identify customer needs and opportunities to increase revenue. Additionally, AI-powered forecasting models enable businesses to accurately predict future demand and optimize inventory levels. Finally, AI has become a valuable tool for customer retention, as it provides insights into churn risk and helps organizations retain subscribers.
As AI continues to evolve, product managers and the product development team must stay informed on the latest trends and technologies to ensure their products remain competitive in the market. Integrating AI into product roadmap planning can help companies maximize value from their data and create amazing customer experiences.
Ultimately, AI provides an unprecedented level of insights and automation for product management, enabling businesses to gain a competitive edge and maximize value for their customers.
Embracing the Future of AI-Driven Product Management
As technology advances and customer expectations become more demanding, product managers must stay ahead of the curve by utilizing AI-driven tools. AI can be used to identify customer needs, anticipate market trends, forecast demand, and optimize product offerings. Integrating AI into product roadmap planning enables businesses to make decisions faster, create new revenue streams, and provide customers with incredible user experiences. Furthermore, AI provides PMs with the analytical skills product managers need.
By leveraging the power of AI, product managers can create smart products that meet customer needs while gaining valuable insights from their data. AI helps businesses stay ahead of the competition and maximize ROI from their product offerings. It’s essential for businesses to understand the potential of AI and how it fits into their product roadmap strategy in order to remain competitive in today’s market.

