Data democratization: How data architecture can drive business decisions and AI initiatives
Introduction
The digital revolution in data management was also called “Digital Transformation” five years ago. It is often described in terms of improving data access but the transformation involves much more. Data democratic systems are useful when they simplify data stacks, eliminate data gatekeepers and allow different teams to access data on to their data platform through streamlined data dashboards. Beyond technical aspects, they have more ambition. When properly democratized data provides employees with information to work on it. Let’s delve deeper into the concept of data democratization and its impact on modern business practices.
What is Data Democratization?
Data democratization refers to the process of making data accessible to non-technical users without requiring the intervention of IT specialists or data scientists. This concept, data democracy, is based on the idea that data should be available and understandable to the average end-user as a part of empowering individuals and ensuring that decisions are data-driven.
The five key aspects of data democratization include:
- Accessibility: Ensuring that data is easily accessible to all relevant stakeholders in an organization, regardless of their technical expertise.
- Usability: Data should be presented in a way that is understandable and usable for people who may not have a background in data analysis.
- Empowerment: By having access to data, employees at all levels can make informed decisions, leading to increased innovation and efficiency.
- Data Governance and Security: While making data accessible, it is also crucial to maintain data privacy, security, and compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
- Tools and Technology: Implementing user-friendly tools and technologies that can help non-technical users to analyze and interpret data effectively.
The goal of data democratization is to move data assets allow for more informed decision-making across all levels of an organization by breaking down the barriers that traditionally limited access to data to specific data professionals or departments.
Why is data democratization important?
Data democratisation helps companies to make informed decisions using technology to provide access to, use and communicate data and the technology can be easily applied.
What does democratize the data mean?
Data democratization is an act that allows for everyone access to data. Thus, each person will have an easy way of obtaining data sharing and interpreting data without having to invest in specialized IT skills.
What is the data democratization strategy?
In an ever changing data environment data democratization strategies have emerged as transformative approaches. It is basically a technique which enables everyone in an organisation to leverage data, no matter technical proficiency.
What Business Challenges Does Data Democratization Address?
By making data management more accesible and usable across in an organization, addresses key buinsess challenges, such as data and reporting requests such as:
- Improved Decision-Making: When data is democratized, employees at all levels have access to relevant information, enabling them to make more informed decisions. This collective insight can lead to better business strategies and operational improvements.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Democratized data fosters a culture of collaboration. Different departments and teams can easily share and interpret data, leading to a more integrated approach to solving business problems.
- Increased Agility and Responsiveness: Organizations can respond more quickly to market changes and customer needs because employees have the data they need to react and adapt in real-time.
- Reduced Bottlenecks: In traditional setups, requests for data analysis are funneled through specialized data teams, creating bottlenecks. Democratization eliminates this by allowing non-specialists to access and analyze data themselves.
- Fostering a Data-Driven Culture: Democratization embeds the use of data into the organizational culture. This shift encourages everyone to base their actions and decisions on data, leading to a more objective and results-focused environment.
- Empowering Employees: Giving employees access to data empowers them and can lead to increased job satisfaction as they feel more valued and capable of contributing meaningfully to the organization’s goals.
- Innovation and Creativity: With easier access to data, employees across the organization can identify new opportunities, trends, and areas for improvement, fostering innovation and creative problem-solving.
- Reducing Dependency on IT and Data Teams: Democratization reduces the reliance on specialized IT and data teams for data queries and reports, allowing these teams to focus on more strategic tasks.
- Cost Efficiency: By enabling more people to access and use data, organizations can reduce the costs associated with reliance on a small number of data professionals.
- Enhanced Customer Experiences: With broader access to customer data, teams can better understand customer needs and preferences, leading to improved products, services, and customer experiences.
Overall, this data democratization means it can transform an organization by making it more agile, informed, and collaborative, thereby enhancing its ability to compete in a data-driven world.
What are the 4 ways to democratize data science?
They offer an opportunity to democratize information processing beyond the confines of computer systems. But democratization must be based on four components: data governance practices, data architecture, data safety and data security.
What is Data Governance? Framework and Examples
Data governance refers to the management of the availability, usability, integrity, and security of the data in enterprise systems, based on internal data standards and policies that also control data usage. Effective data governance ensures that data is consistent and trustworthy and doesn’t get misused. It’s a key part of regulatory compliance, especially important in data-sensitive fields like banking, healthcare, and government to name a few.
Framework of Data Governance
A data governance framework involves several components:
- Policies and Standards: Setting up clear policies and standards for data management. This includes how data is collected, stored, processed, and disposed of.
- Data Quality: Ensuring the accuracy, completeness, and reliability of data. This involves processes and tools for data cleaning, validation, and enrichment.
- Data Access and Security: Managing who has access to data and protecting it from unauthorized access. This includes implementing data security measures and access control mechanisms.
- Compliance and Risk Management: Ensuring that data usage complies with relevant laws and regulations, such as GDPR for personal data in Europe. This involves regular audits and risk assessments.
- Data Stewardship: Assigning roles and responsibilities for data management. Data stewards are responsible for overseeing data quality, access, and policy enforcement.
- Data Architecture and Integration: Establishing a suitable architecture for data storage and integration. This includes decisions on databases, data warehouses, and ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes.
- Change Management: Managing changes in data governance policies, processes, and technologies.
- Performance Measurement: Using metrics and KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) to assess the effectiveness of data governance initiatives.
Examples of Data Governance in Practice
- Financial Services: Banks use data governance to ensure the accuracy and security of financial transactions and to comply with regulations like the Sarbanes-Oxley Act.
- Healthcare: Hospitals implement data governance to manage patient records, ensuring they are accurate and only accessible to authorized personnel, in compliance with HIPAA regulations.
- Retail: A retail company might use data governance to manage customer data, ensuring it is accurate, securely stored, and used in compliance with privacy laws like GDPR.
- Government: Government agencies use data governance to manage public data, ensuring transparency, accuracy, and adherence to public records laws.
- E-Commerce: E-commerce platforms implement data governance to handle customer data, transaction data, and to ensure compliance with various e-commerce regulations and standards.
(Data governance strategy is crucial in a data-driven world where companies rely heavily on information to make decisions, drive processes, and comply with legal requirement
Core Benefits of Data Democratization
Democratizing information within an organization, where all data sets and insights are made accessible and understandable to all employees, regardless of their technical skills or department, can offer numerous benefits. Here are five key advantages:
- Enhanced Decision Making: When information is democratized, employees at all levels have access to the data they need to make informed decisions. This access can lead to better decision-making across the organization, as employees are no longer reliant on a small group of data specialists to interpret and share insights. This results in a more agile and informed workforce.
- Increased Innovation: Democratized data can spark innovation as it allows employees from different departments to access and analyze data in new ways. When employees with diverse perspectives have access to the same information, they can collaborate more effectively and come up with innovative solutions to business challenges.
- Improved Employee Engagement and Empowerment: Providing employees with access to data makes them feel more valued and empowered. It fosters a culture of trust and transparency, as employees understand they are being given the tools and information they need to succeed in their roles. This can lead to higher levels of employee engagement and satisfaction.
- Efficiency and Productivity Gains: Democratized information can lead to significant efficiency and productivity improvements. Employees spend less time waiting for data requests to be fulfilled by IT or data teams and can instead access the information they need when they need it. This reduces bottlenecks and speeds up the process of turning data into actionable insights.
- Better Risk Management and Compliance: When more eyes are on the data, organizations can more easily identify and mitigate risks, including data quality issues, potential compliance breaches, and operational inefficiencies. This broader oversight can help ensure that the organization adheres to industry regulations and standards, reducing the risk of costly fines and reputational damage.
By democratizing information, organizations not only optimize their operations but also foster a more inclusive and collaborative work environment. This approach right data also aligns with the modern trend towards transparency and data-driven cultures in the business world.
Why data democratization is crucial to your business
Companies with no data visualization tools or employees having the ability or training in using data face a wide variety of challenges. These problems arise because the data cannot be accessed. This problem can easily be solved with data democraticization. The solution empowers employees to use data analysis for their daily business tasks.
The challenges faced by companies without enough data analysts and employees trained or skilled in using data are multifaceted and can significantly impact their competitiveness and efficiency. In the modern business environment, data plays a crucial role in decision-making, understanding market trends, customer behavior, and optimizing operations. When a company lacks this capability, it confronts several specific problems:
- Inability to Make Data-Driven Decisions: Without access to data analysis, companies rely on intuition or outdated methods for decision-making. This approach can lead to suboptimal choices that don’t reflect current market conditions or customer needs.
- Missed Opportunities for Innovation: Data analytics often reveals insights that can drive innovation in products, services, and processes. Companies lacking in this area may miss these opportunities, allowing competitors to gain an edge.
- Inefficient Operations: Data analytics helps in optimizing operations, identifying inefficiencies, and reducing costs. Without these insights, companies may operate less efficiently, impacting profitability.
- Poor Customer Understanding: Understanding customer preferences, behaviors, and trends is key to successful marketing and product development. Lack of data analysis means a company may not fully understand its customers, leading to less effective strategies.
- Risk Management Issues: Data analysis plays a crucial role in identifying and mitigating risks. Companies that can’t analyze their data might be exposed to higher operational, financial, and reputational risks.
The solution to these challenges lies in democratizing data within the organization. Data democratization refers to making data accessible to non-technical employees, allowing them to use data in their day-to-day work. This process involves data democratization requires several key steps:
- Investing in User-Friendly Tools: Implementing data analysis tools that are easy to use for non-specialists. These tools should allow employees to extract, analyze, and visualize data without needing advanced technical skills.
- Training and Education: Providing training to employees on how to use these tools effectively. This training should focus not only on how to use the tools but also on understanding the basics of data analysis and interpretation.
- Creating a Data-Driven Culture: Encouraging a culture where decisions are based on data rather than intuition. This cultural shift requires support from top management and involves changing how decisions are made throughout the organization.
- Ensuring Data Quality and Accessibility: Making sure that the data is accurate, up-to-date, and easily accessible to those who need it. This step involves setting up proper data governance and management practices.
- Addressing Privacy and Security Concerns: Ensuring that democratization doesn’t compromise data security and privacy. Employees should be trained on the importance of data privacy and the legal implications of data handling.
By democratizing data, companies can empower their employees to further analyze data independently make informed decisions, innovate more effectively, operate efficiently, understand customers better, and manage risks more effectively. This approach not only resolves the challenges of not having data-skilled employees but also transforms the organization into a more agile, informed, and competitive entity in the marketplace.
Key considerations for data democratization
As companies transition towards a digitalized organizational culture and build infrastructures to support data literacy, they will encounter both benefits and potential hazards. The main benefits of such a transformation include:
- Improved Decision-Making: With enhanced data literacy, companies can make more informed decisions. Data-driven insights can lead to better strategies, enhanced product development, and more efficient operational processes.
- Increased Agility: Digitalization allows companies to quickly adapt to market changes. They can leverage real-time data to respond to emerging trends, customer behaviors, and competitive threats more rapidly.
- Enhanced Customer Insights: Data literacy enables deeper understanding of customer needs and preferences, leading to more effective marketing strategies, personalized customer experiences, and improved customer satisfaction.
- Operational Efficiency: By utilizing data, companies can identify inefficiencies in their operations, streamline processes, and reduce costs, resulting in higher profitability.
- Innovation and Growth: Access to and understanding of data can spark innovation, leading to the development of new products, services, and business models that drive growth.
- Empowered Employees: Employees equipped with data literacy skills feel more empowered and engaged, as they can contribute more effectively to the company’s goals.
However, alongside these benefits, companies may face several challenges:
- Cultural Resistance: Shifting to a data-driven culture can be met with resistance from employees who are accustomed to traditional ways of working. Overcoming this requires strong leadership, effective change management, and ongoing support.
- Data Privacy and Security Risks: As data usage increases, so does the risk of data breaches and privacy violations. Companies must ensure robust data security measures and comply with data protection regulations.
- Skill Gaps: The need for data literacy can highlight skill gaps within the workforce. Addressing this requires significant investment in training and potentially hiring new talent with the requisite skills.
- Data Quality and Integration Issues: Ensuring the quality and integration of data from various sources can be challenging. Poor data quality can lead to incorrect insights and decisions.
- Costs of Digital Transformation: The initial investment in technology, training, and change management can be substantial. Companies must balance these costs against the expected long-term benefits.
- Overdependence on Data: There’s a risk of becoming overly reliant on data, potentially overlooking the value of human intuition and experience. A balance between data-driven insights and human judgment is crucial.
In conclusion, while the move towards digitalization and data literacy offers substantial benefits in terms of decision-making, efficiency, innovation, and customer insights, it also presents challenges related to cultural adaptation, data security, skill requirements, and cost. Successfully navigating these challenges requires a strategic approach, balancing the benefits and risks while fostering a culture sensitive data, that embraces both data and human insights.
A more productive workforce
Similar results showed that 77% of companies who engaged in data upskilling experienced a 70% increase in the quality of decision-making, innovation, customer satisfaction and employee retention. Data democratization can improve the efficiency and innovation of our workforces. A good example of democratizing data is the case of Allianz. During its datacamp program, Allies has trained nearly 4,000 workers to improve their knowledge in various areas of self service analytics.
Case Studies on Data Driven Decisions
- Netflix’s Personalized Recommendations: Netflix, the streaming giant, uses data-driven algorithms to provide personalized movie and TV show recommendations. By analyzing viewer habits, preferences, and ratings, Netflix tailors its content to individual users, increasing engagement and customer satisfaction. This approach not only keeps subscribers hooked but also guides Netflix in deciding which new content to produce.
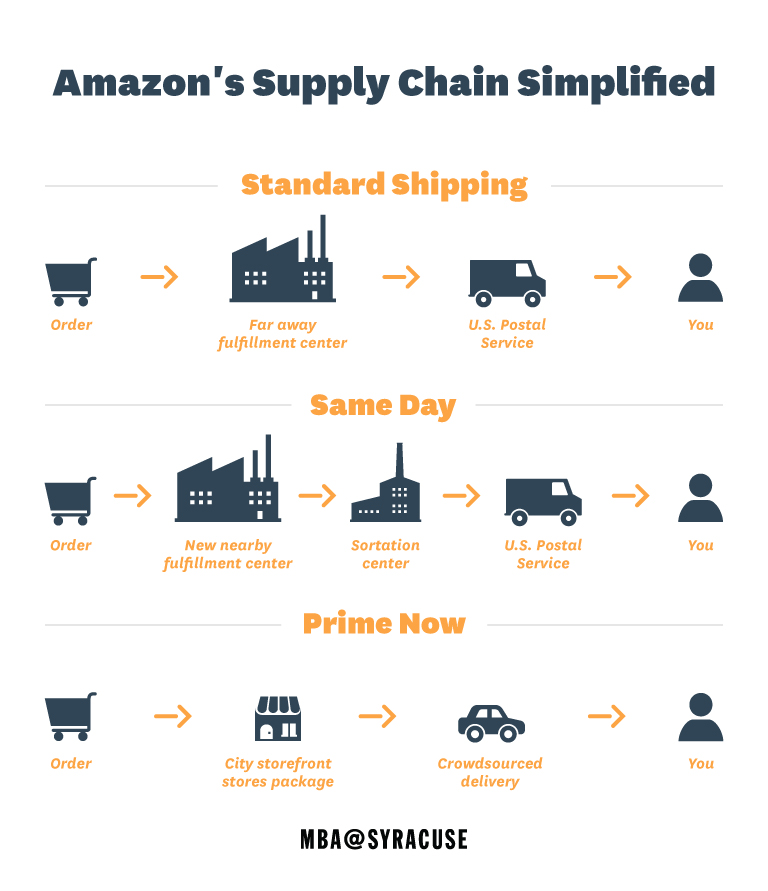
- Amazon’s Supply Chain Optimization: Amazon uses data analytics extensively to optimize its supply chain and delivery systems. By analyzing customer purchasing patterns, geographic sales data, and inventory levels, Amazon efficiently manages its stock, reducing overhead costs and improving delivery times. This data-driven approach has been key to Amazon’s ability to offer same-day or next-day delivery on many items

Sources:
https://www.lepide.com/blog/what-is-data-democratization/

