Introduction:
In the rapidly evolving landscape of modern business, Artificial Intelligence (AI) stands as a beacon of transformative power. It is the new buzzword in the business community, and rightfully so. This technology was once a distant dream but now it is a tangible and integral part of our daily operations. From automating mundane tasks to pioneering innovation, AI’s footprint is indelible. In this article, “Artificial Intelligence, Back to the Basics” I dive deep into the essence of AI, unraveling its complexities and showing its potential in enhancing prediction accuracy and efficiency. Join me as I explore the fundamental concepts and real world applications of AI, illuminating its role as a catalyst for business revolution.
How is AI used in business?
AI is being used throughout businesses across the globe for automating work tasks, improving data analysis, and making better decisions quicker. A growing trend in the industry is the use of AI tools such as ChatGPT, Machine learning and Deep Learning.
Businesses Are Using AI To Improve the Customer Experience
The use of AI is important in improving the customer experience on touch points. Forbes Advisor reports that 75% of organizations now use chatbots. Interestingly 77% of businesses utilize AI to improve e-mails, while 51% employ it for personalization, which includes recommendation of product information. A company may also be using AI to create long-term writing content including webpages (41%) e.g. personal advertising (46%). In fact, the number of users of AI in phone-call answering is 45%. 45% are using AI to improve their SMS.
AI for personalized customer services, experiences and support
AI can be used to provide personalized customer service and experience to customers across many industries. This uses customer identifiers and consolidated information from multiple systems for identifying who the user is. Although it’ s widely accepted to use AI in this manner, Earley says companies are still capable. I believe personalization doesn’t happen as quickly as we’d hoped and not as easily.
Data Analysis and Insights
The artificial intelligence can analyze vast quantities of data that human scientists couldn’t manually analyze. From customer interactions with the shippers to marketing information to effective marketing campaigns, all these data will give you detailed insight into your company’s performance for better performance. Big Data and artificial intelligence allow algorithms to analyze data sets rapidly, saving time and energy.
Business Processes Artificial Intelligence Is Improving
Artificial intelligence helps organizations become more agile and efficient. According to a recent Forbes advisor survey, AI has been used to manage various business functions and activities. The majority of enterprises are employing machine learning to improve production processes, while 51% use it to improve process automation and 52% use it for SEO and keyword research. A large share of businesses use AI to gather and analyze information (40% of companies), create new ideas (38%). AI will also streamline the internal communication plan presentation and report (46%). Business also employs artificial intelligence (31%) to write web pages (39% of the total).
What is the future of AI in business?
It is estimated that AI will automate nearly 70 pcs jobs and create billions of new jobs globally between 2021 and 2030 and increase economic productivity and profitability globally. McKinsey, 14 June 2023.
The Majority of Business Owners Expect AI Will Have a Positive Impact on Their Business
Several companies say artificial intelligence is useful for their companies.. Most respondents predicted that the use of artificial intelligence would help improve sales performance and improve sales relationships. AI is seen as a valuable asset in enhancing decisions (42%), decreasing response time (32%), and preventing mistakes (48%). The companies expect AI to be in the process of improving their work processes (42%).
The Game-Changing Role of AI in Business:
Artificial Intelligence, herein referred to as AI, can be a game-changer for companies, and there are a couple of fundamental reasons why that is. AI reduces the cost of prediction. Dr. Ajay Agarwal, Avi Goldfarb, and Joshua Gans, in their book “Prediction Machines,” explain how AI, more specifically, machine and deep learning models, reduces the cost of making predictions. In this context, a prediction fills in missing information based on already known information. In practical terms, this can mean improved decision-making, new avenues for business opportunities and customer relationships, and substantial efficiency gains. Let’s dive a little deeper into each of these.
How many businesses are using AI?
Over 90% are currently using AI in their businesses. Many companies adopt artificial intelligence for their marketing strategy. 73% think AI is their top priority.
How does AI work in digital business?
AI-powered software allows the simulation or testing of multiple scenarios to aid product design, optimization or prediction modeling. In order to improve competitive advantages organisations need to be more efficient in a digital world.
Three Types of AI
The company needs to view AI from a business perspective, and not from a technological perspective. AI can be used to support a number of business processes: automate processes by gaining insights through data analysis.
Enhancing Decision-Making with Artificial intelligence
Improved decision-making implies that because predictions are more accurate and cheaper, it becomes easier for businesses many organizations and individuals to make informed decisions.
The Role of Accurate Predictions in Business Processes
Organizations can better predict consumer behavior through customer communications and marketing campaigns through the use of Large Language Models, or, to be more specific, Tesla, using big data through measuring your vehicle telemetry and feedback you give whenever auto-pilot is disabled, can train a model on that data to provide a continuous improvement mechanism. Lower prediction costs open up new business models and services. For instance, autonomous vehicles rely heavily on AI’s ability to predict traffic conditions, pedestrian movement, and potential hazards. With more accurate predictions, resources can be allocated more efficiently. 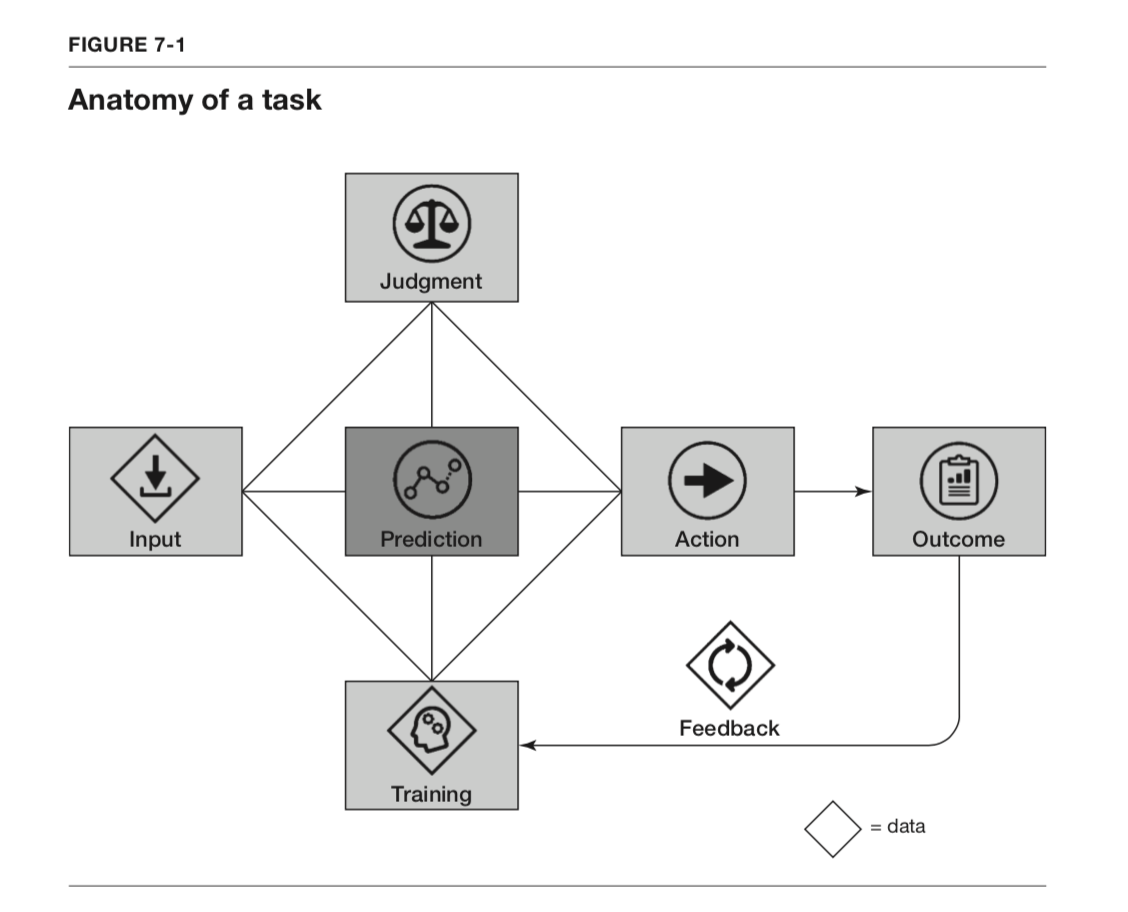 This diagram represents the workflow of a task within a machine learning context, referred to as the “Anatomy of a task”. It begins with “Input”, where data is fed into the system, followed by “Prediction”, where the model processes the input to make a forecast or decision. The “Action” phase is where a tangible operation is performed based on the prediction, leading to an “Outcome”, the result of the action taken. “Feedback” is then provided based on the outcome, which is used to “Train” the model, thereby improving its future predictions and actions. The cycle suggests a continuous process of learning and adaptation, enhancing the model’s judgment over time.
This diagram represents the workflow of a task within a machine learning context, referred to as the “Anatomy of a task”. It begins with “Input”, where data is fed into the system, followed by “Prediction”, where the model processes the input to make a forecast or decision. The “Action” phase is where a tangible operation is performed based on the prediction, leading to an “Outcome”, the result of the action taken. “Feedback” is then provided based on the outcome, which is used to “Train” the model, thereby improving its future predictions and actions. The cycle suggests a continuous process of learning and adaptation, enhancing the model’s judgment over time.
The Role of Accurate Predictions in Healthcare
In sectors like healthcare, AI can predict disease outbreaks or patient deterioration, enabling proactive rather than reactive responses. The AI will do that using historical and current data synthesized by experts. AI is only inherently intelligent once it has an excellent initial training data set. An AI model is only as good as the data you give it. Once it has that data, it will start to “have a mind of its own, if you will ” and make predictions based on the data you have fed the model.
Introduction to the Confusion Matrix:
Before we dive deeper into the basics, there is one more concept that is imperative to understand: the Confusion Matrix. The Confusion Matrix is the cost of getting those predictions wrong or right. It is a critical tool for evaluating machine and deep learning and models, particularly classification tasks. It relies on four fundamental principles: True Positive, True Negative, False Positive, and False Negative. 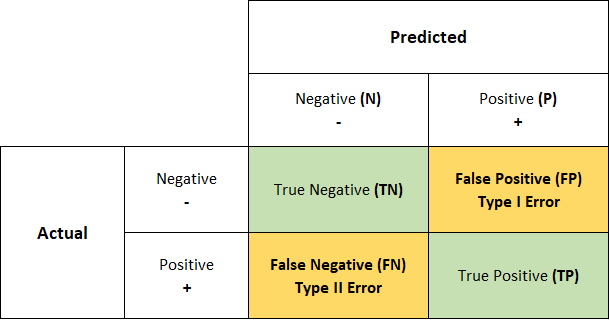 The diagram shows a Confusion Matrix, a tool used in machine learning to evaluate the performance of classification models. It shows four outcomes of predictions: True Negatives (TN) and True Positives (TP) represent correct predictions for the negative and positive classes, respectively. False Positives (FP), or Type I Errors, occur when the model incorrectly predicts the positive class, and False Negatives (FN), or Type II Errors, happen when the model incorrectly predicts the negative class. This matrix helps in understanding the accuracy of a model by contrasting the predicted versus actual outcomes.
The diagram shows a Confusion Matrix, a tool used in machine learning to evaluate the performance of classification models. It shows four outcomes of predictions: True Negatives (TN) and True Positives (TP) represent correct predictions for the negative and positive classes, respectively. False Positives (FP), or Type I Errors, occur when the model incorrectly predicts the positive class, and False Negatives (FN), or Type II Errors, happen when the model incorrectly predicts the negative class. This matrix helps in understanding the accuracy of a model by contrasting the predicted versus actual outcomes.
Understanding True Postives:
An actual or true positive means the AI model has correctly predicted the outcome. An example is when a medical test is conducted, it correctly identifies the patients with the disease.
The Role of True Negatives:
A true negative occurs when the model accurately predicts the flip side of that or the negative class. In the same medical test scenario, a true negative correctly predicted the patients who do not have the disease.
False Positives and Type I Error
A false positive is when the model incorrectly predicts the outcome. In our same medical test scenario, a false positive is that it incorrectly indicates that a patient has the disease when, in reality, they do not; they are actually a healthy patient. This is also known as a Type I error. These can be particularly problematic and save many human resources and time spent elsewhere.
False Negatives and Type II Error
A false negative is when the model incorrectly predicts the flip side of that or more data in the negative class. In our scenario, this could mean that the model completely fails in identifying the patient with the disease. This is known as a Type II error. False negatives can be dangerous, particularly in medical diagnosis, as they might lead to a lack of treatment for an existing condition.
The AI Effect and its implications:
Let’s now transition to some key concepts that Dr. Sheen S. Levine, an Associate Professor at the Naveen Jindal School of Management, UT Dallas, mentioned in his Artificial Intelligence Innovation class. First, you must understand that GPTs (General Purpose Technology) can be used in a wide range of sectors/industries and have spillover effects that will also affect human development, societies, and the economy. GPTs use Intelligence to take in/integrate information in novel ways during varying circumstances. AI itself is machines evaluating human thoughts. The AI effect means that when a machine can do something, it’s no longer considered Intelligence. A classic example of the AI effect is the game of chess. For many years, chess was considered a hallmark of human Intelligence. The game requires you to use foresight, strategic thinking, foresight, and decision-making skills. But, in 1997, IBM’s Deep Blue defeated world chess champion Garry Kasparov. This landmark moment for the AI world showed how AI can outperform humans in strategic thinking tasks. After this event, The narrative changed from “only intelligent beings can play chess” to “chess is just a set of mathematical calculations well-suited for computers.”
Case Studies and Infographics:
American Airlines’ Smart Gating Technology
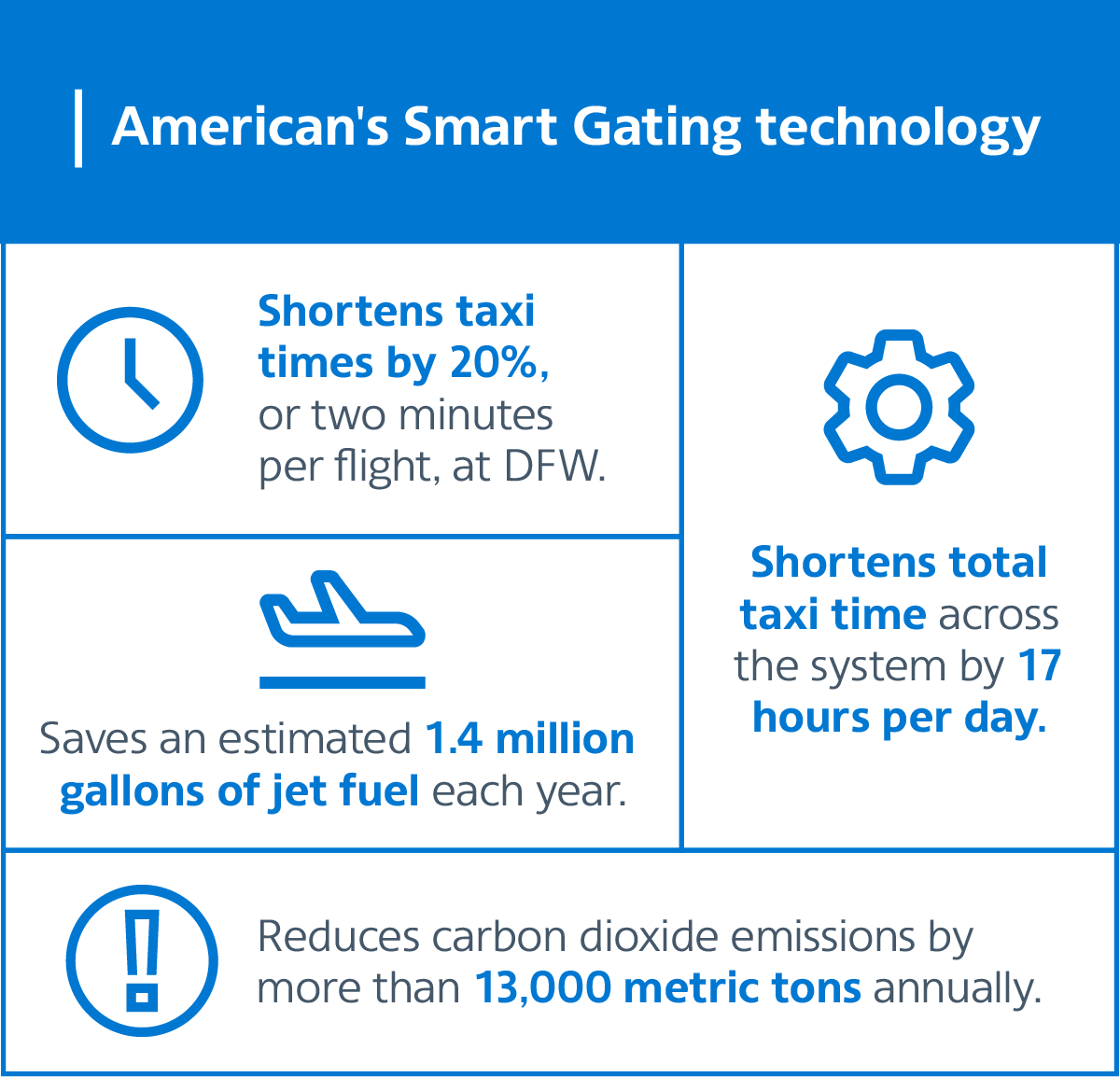 In the fast-paced world of aviation, efficiency and time management are paramount. Recognizing this, American Airlines took a significant leap forward during the holiday season by introducing an innovative Smart Gating technology. This cutting-edge tool represents a fusion of the technology experts American’s IT and Operations teams’ expertise, showcasing how artificial intelligence (AI) and smart algorithms can transform everyday challenges into streamlined processes. According to American Airlines, at its major hubs like DFW, “the tool has helped the carrier shorten aircraft taxi times at DFW by 20% or about two minutes per flight. Those minutes add up — Smart Gating has helped American reduce the amount of time its aircraft spend taxiing at DFW by more than 11 hours each day” (American Newsroom, Straight to the gate this holiday season).
In the fast-paced world of aviation, efficiency and time management are paramount. Recognizing this, American Airlines took a significant leap forward during the holiday season by introducing an innovative Smart Gating technology. This cutting-edge tool represents a fusion of the technology experts American’s IT and Operations teams’ expertise, showcasing how artificial intelligence (AI) and smart algorithms can transform everyday challenges into streamlined processes. According to American Airlines, at its major hubs like DFW, “the tool has helped the carrier shorten aircraft taxi times at DFW by 20% or about two minutes per flight. Those minutes add up — Smart Gating has helped American reduce the amount of time its aircraft spend taxiing at DFW by more than 11 hours each day” (American Newsroom, Straight to the gate this holiday season).
Development and Implementation:
American Airlines developed Smart Gating technology to address a trio of critical operational challenges: gate conflicts, ramp congestion, and taxi times. By utilizing advanced AI algorithms, the technology dynamically assigns aircraft to the nearest available gate. This proactive approach is not only about finding an empty gate but also about considering several factors, such as the turnaround time, the type of aircraft, and the proximity to the aircraft’s next departure gate.
Impact on Operations:
The impact of this technology has been profound. The smart gating system has significantly reduced gate conflicts, where two aircraft are assigned to the same gate. This reduction in gate conflicts leads to a smoother operation and improved customer experience. Moreover, by assigning gates more efficiently, the technology has played a crucial role in reducing ramp congestion. This is particularly crucial during peak travel times when airport traffic is at its highest.
Environmental and Economic Benefits:
Another remarkable competitive advantage of this technology is its contribution to environmental sustainability. By shortening taxi times, the Smart Gating system has helped in reducing fuel consumption and, consequently, the carbon footprint of the airline’s operations. Economically, this translates into cost savings for the airline, while environmentally, it represents a step towards more sustainable aviation practices.
Future Perspectives:
Looking ahead, the success of Smart Gating technology opens up new possibilities for AI in the aviation industry. It serves as a case study for other airlines companies and airports looking to optimize operations. Furthermore, it highlights the potential of AI to not only streamline processes but also to contribute positively to environmental sustainability and customer satisfaction. To read more about American Airlines Smart Gating technology, visit https://news.aa.com/news/news-details/2023/American-is-using-machine-learning-to-keep-its-hubs-moving-this-holiday-season-OPS-DIS-12/default.aspx
PayPal’s Fraud Detection Challenge:
Background of PayPal’s Fraud Detection Challenge:
- Problem Statement: As one of the largest online payment platforms, PayPal processes millions of transactions daily. With this volume, the company faces a substantial risk of fraudulent activities, which can lead to significant financial losses and damage to customer trust.
- Traditional Methods: Initially, PayPal relied on traditional rule-based systems for fraud detection. These systems would flag transactions based on predefined criteria, but they struggled with the complexity and evolving nature of fraud.
Implementation of AI in Fraud Detection:
- Introduction of Machine Learning: To enhance its fraud detection capabilities, PayPal turned to machine learning algorithms. These algorithms are capable of analyzing vast amounts of transaction data in real time, learning from patterns, and adapting to new types of fraudulent activities.
- Data Analysis: The AI system examines various aspects of each transaction, including the amount, the location of the buyer and seller, the device used for the transaction, and the transaction history of the involved parties.
- Behavioral Analysis: The system also uses behavioral analysis to understand typical user patterns, helping to identify anomalies that may indicate fraud.
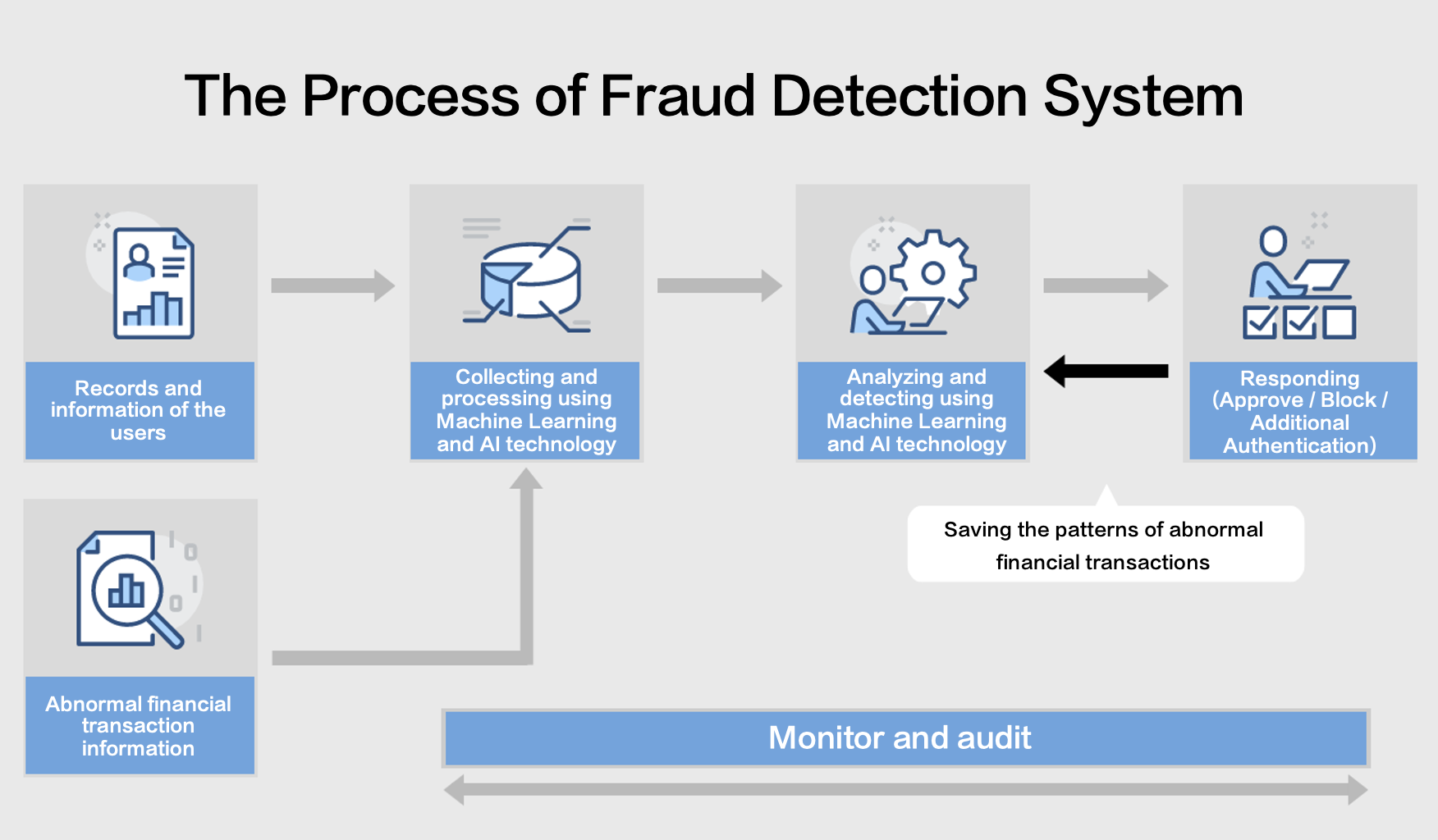 This diagram illustrates the process automation workflow of a Fraud Detection System (FDS) that utilizes Machine Learning and AI technology. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of the process depicted:
This diagram illustrates the process automation workflow of a Fraud Detection System (FDS) that utilizes Machine Learning and AI technology. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of the process depicted:
- Records and Information of the Users:
- The first step involves gathering the users’ personal and transactional data. This information forms the base for the system to understand normal user behavior patterns.
- Collecting and Processing Using Machine Learning and AI Technology:
- This data is then fed into the AI system where machine learning algorithms process the information. The AI system is trained to identify patterns and behaviors that are indicative of normal and fraudulent activities.
- Analyzing and Detecting Using Machine Learning and AI Technology:
- In this phase, the processed data is analyzed to detect any anomalies or signs of fraud. The system uses historical and real-time data to spot inconsistencies that could suggest fraudulent transactions.
- Responding (Approve / Block / Additional Authentication):
- Once a potential fraud is detected, the system decides on the appropriate action. It may approve the transaction if it seems legitimate, block the transaction if it is likely fraudulent, or request additional authentication to verify the user’s identity.
- Saving the Patterns of Abnormal Financial Transactions:
- The system records the details of detected fraudulent activities. These patterns are saved and used to refine the AI model, enhancing its accuracy for future fraud detection.
- Monitor and Audit:
- The last step involves continuous monitoring and auditing of transactions to ensure the system is working as intended and to make any necessary adjustments. This helps in maintaining the integrity of the fraud detection process.
The cyclic arrows between the “Analyzing and Detecting” and “Monitor and Audit” stages of business process emphasize that this process is iterative; the system continuously learns and improves from each transaction. The flow from “Responding” back to “Analyzing and Detecting” indicates that the outcomes of transactions, whether approved, blocked, or subjected to additional authentication, also feed back into the system for ongoing learning and optimization of business functions. This ensures that the FDS remains dynamic and adaptive to emerging fraud tactics.
Outcomes and Results:
- Reduction in Fraud: PayPal has reported a significant decrease in fraudulent transactions since implementing AI, demonstrating the effectiveness of machine learning in identifying and preventing fraud.
- Improved Accuracy: The AI system has a lower rate of false positives compared to traditional methods. This means legitimate transactions are less likely to be incorrectly flagged as fraudulent, enhancing the user experience.
- Adaptability: The machine learning models continually adapt to new fraud tactics. As fraudsters evolve their methods, the AI system learns and adjusts, maintaining a high level of security.
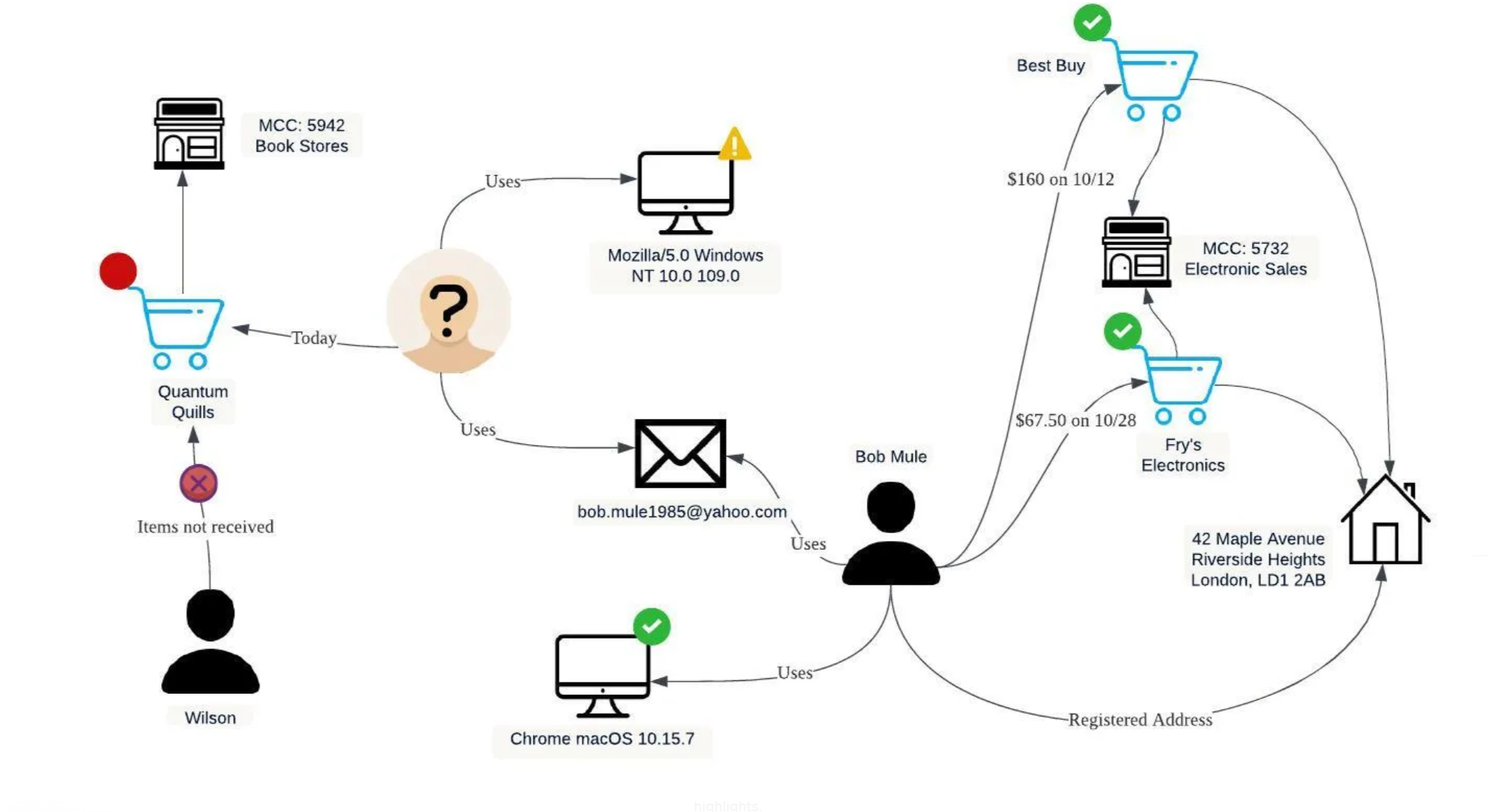 The image depicts a scenario where a user, identified as “Bob Mule,” is involved in a series of transactions that raise flags of potential fraudulent activity within a PayPal-like system. The graphic is a representation of a fraud detection system in action, analyzing transaction patterns to safeguard account holders. Here’s an expanded explanation based on the image:
The image depicts a scenario where a user, identified as “Bob Mule,” is involved in a series of transactions that raise flags of potential fraudulent activity within a PayPal-like system. The graphic is a representation of a fraud detection system in action, analyzing transaction patterns to safeguard account holders. Here’s an expanded explanation based on the image:
- Unverified Device and Unusual Purchase Patterns:
- The system has detected a transaction initiated from an unverified device using Bob’s PayPal account. The device runs on “Mozilla/5.0 Windows NT 10.0”, which is different from Bob’s usual device running “Chrome macOS 10.15.7”. This discrepancy suggests that someone other than Bob may be using the account.
- Atypical Merchant Category:
- Bob’s account is used to make a purchase from “Quantum Quills” under the merchant category code (MCC) 5942, which is associated with bookstores. The transaction is flagged because Bob has no history of purchasing from this category, indicating an anomaly in his buying behavior.
- Non-Delivery Complaint:
- To compound the suspicion, there is a complaint filed by a customer named Wilson claiming that items from Quantum Quills were not received. This could indicate that the transaction is part of a fraudulent scheme.
- Comparison with Verified Transactions:
- The diagram contrasts this suspicious activity with verified transactions from Bob’s account, which include purchases from Best Buy and Fry’s Electronics, both under MCC 5732 for electronic sales, with a clear history of deliveries to Bob’s registered address at 42 Maple Avenue.
- Email Link:
- An email address (bob.mule1985@yahoo.com) is associated with the unverified device, potentially linking the suspicious transaction to a specific individual or indicating the account’s compromise.
- Fraud Detection Actions:
- In response to these red flags, the fraud detection system may take preventive actions such as blocking the transaction, alerting the account holder, or requiring additional authentication to verify the legitimacy of the transaction.
The depicted process is a snapshot of how sophisticated fraud detection systems work in real-time to protect users from unauthorized account access and fraudulent transactions. By comparing current transactions against established patterns and historical data, the system can quickly identify and react to anomalies, ensuring the security of the account and the integrity of the financial platform.
Future Implications and Innovations:
- Continued Evolution: PayPal continues to invest in AI and machine learning to stay ahead of sophisticated fraud schemes.
- Broader Applications: The success of AI in fraud detection at PayPal serves as a model for other financial institutions facing similar challenges.
- Enhanced Customer Trust: By effectively reducing fraud, PayPal not only protects its financial interests but also bolsters customer confidence in the platform.
This case study exemplifies the transformative impact AI can have in the financial sector, particularly in areas requiring quick, accurate decision-making based on large volumes of data. The success at PayPal has set a benchmark in the industry for using AI to combat online fraud.
Conclusion:
In the rapidly evolving landscape of technology, Artificial Intelligence stands out as a transformative force. Its integration into systems and processes promises to revolutionize not only routine and repetitive tasks but also complex cognitive functions and human jobs that require learning and adaptation. The real prowess of an AI model hinges on the quality and breadth of its training data, which determines its predictive accuracy and decision-making capabilities. As we stand on the cusp of this AI-driven era, it is imperative for businesses and organizations to contemplate: What strategies will you implement to harness the power of AI, and how will the data at your disposal shape your business strategy and future competitive edge?

