Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) promises profound transformation, yet many C-level executives remain cautious, and rightly so. The landscape is littered with AI initiatives that have failed to deliver on their promises, often due to their inherent complexity, significant resource demands, and pervasive data challenges. This article aims to address that skepticism directly by presenting low-code and no-code (LCNC) platforms not as another technological buzzword, but as a pragmatic and powerful pathway to unlock AI’s true business value. We will explore how LCNC simplifies AI integration, democratizes its access, and delivers measurable return on investment, shifting AI from a specialized IT endeavor to a pervasive, accessible business capability that drives agility, cost efficiency, and competitive differentiation across the enterprise.
I. The AI Imperative: Navigating Executive Skepticism
The Current State of AI Adoption and Its Pitfalls
Artificial Intelligence holds profound transformative potential across industries, driving innovation and efficiency. Yet, despite this promise, a significant majority of AI projects unfortunately fail to deliver on their promises, leading to disappointing outcomes for many organizations. This high failure rate is a critical concern for C-level executives, who must justify significant investments and manage organizational change.
Leading industry reports consistently corroborate this challenge. Gartner reports a staggering 85% failure rate for AI projects. This alarming statistic highlights the significant challenges inherent in AI deployment. Further supporting this, a 2023 McKinsey report indicates that 70% of AI projects fail to meet their goals due to issues with data quality and integration. A study by Forrester Research in 2024 shows that 68% of organizations face significant challenges regarding data quality and integration directly impacts their AI success. Deloitte’s 2024 survey further highlights this issue, as 80% of AI and machine learning projects have reported having data quality and governance difficulties.
These consistent failures across multiple reputable sources such as, Gartner, McKinsey, Forrester, and Deloitte point to a systemic issue that extends beyond individual project mismanagement. It highlights fundamental challenges within traditional AI development and organizational readiness. The primary reasons for these failures within organizations are consistently attributed to poor data quality, inadequate data availability, and a limited understanding of the capabilities of AI. For C-level executives, this validates their skepticism about AI’s reliability and cost-effectiveness, underscoring that the current approach to AI adoption is inherently risky and often unproductive. This situation emphasizes the urgent need for a different, more effective methodology.
Common C-Level Misconceptions About AI
Beyond the documented failure rates, executive skepticism is often fueled by several pervasive misconceptions about AI:
- “AI is too complex and only for tech experts”: Many executives feel intimidated by AI, believing it requires deep technical knowledge or a Ph.D. in computer science to be utilized effectively. This perception creates a significant barrier to widespread adoption beyond specialized IT departments. The common instinct to delegate AI initiatives solely to the IT or digital department, as noted by McKinsey, is often a “recipe for failure”. This delegation, born from a belief that AI is exclusively a technical domain, prevents the necessary strategic alignment and executive sponsorship that are crucial for successful transformation. Without informed leadership, projects can lack clear business goals and wander off course, reinforcing initial skepticism when they falter.
- “AI is just ChatGPT”: The public’s overwhelming focus on generative AI chatbots has led to a narrow understanding of AI’s broader applications. Executives may overlook its diverse potential in areas such as optimization, automation, forecasting, and recommendation systems. This limited perspective can prevent organizations from identifying and pursuing high-value AI use cases. This misconception indicates a broader lack of AI literacy within executive ranks, which restricts their ability to identify varied, impactful AI applications beyond conversational interfaces.
- “AI is only for large enterprises with vast resources”: A prevalent belief is that AI solutions are exclusively beneficial for large corporations with extensive budgets, specialized talent, and significant infrastructure. This deters smaller and mid-sized businesses from exploring AI’s potential, despite the increasing accessibility of AI-as-a-Service platforms.
- “AI guarantees immediate success and overnight transformation”: Some executives green-light AI projects with sky-high expectations or vague success criteria, anticipating instant, magical results. This unrealistic expectation often leads to disappointment and a perception of failure when benefits accrue incrementally over time, requiring strategic planning and continuous adaptation. Rushing into AI without clearly scoping how it addresses a business need frequently leads to meager outcomes, as teams may build models that either solves the wrong problem or no problem at all.
- “AI will replace human jobs”: A pervasive and understandable fear among executives and their workforce is the widespread unemployment caused by AI automation. This concern can lead to employee resistance, a lack of buy-in, and internal friction, hindering successful implementation. However, the prevailing view among experts is that AI is here to support and augment human capabilities, allowing employees to focus on more strategic and creative work, rather than outright replacing them.
- “AI lacks ethical considerations and human oversight”: Worries about AI operating without proper governance, transparency, accountability, or fairness can cause hesitation in adopting AI technologies, especially in regulated industries. Trust in AI systems can be fragile, particularly when they behave unpredictably or rely on opaque processes.
Setting the Stage for LCNC as a Pragmatic Solution
The persistent high failure rates and the prevalence of these misconceptions highlight a critical disconnect: the vast potential of AI is often hindered by the complexities and resource demands of traditional development, coupled with a lack of strategic alignment and understanding within leadership. LCNC platforms emerge as a vital bridge, specifically designed to simplify AI adoption, significantly reduce technical barriers, and empower a broader range of users to leverage AI effectively. They offer a pathway to pragmatic AI implementation that aligns with business goals and delivers measurable value. This transition positions LCNC not as another technological buzzword, but as a strategic enabler that directly addresses the documented challenges and psychological barriers to AI adoption, offering a tangible solution to the problems executives are already experiencing or anticipating.
II. Democratizing Innovation: Understanding Low-Code and No-Code Platforms
Clear Definitions and Distinctions
To fully appreciate the strategic value of LCNC, it is essential to establish clear definitions and distinctions between these two powerful development paradigms. While often used interchangeably, they cater to different user groups and application complexities.
No-Code Platforms: These platforms are specifically designed for non-technical business users, often referred to as “citizen developers” or “business technologists,” to create applications and automate business processes without writing any traditional programming code. They achieve this through highly intuitive visual interfaces such as, drag-and-drop functionalities, form-based configuration panels, and pre-built templates. No-code is typically employed for developing tactical applications that handle simpler, departmental-specific functions, such as internal forms, basic data collection, or straightforward workflow automation.
Low-Code Platforms: While also utilizing visual interface and drag-and-drop capabilities, low-code platforms require some basic coding skills. They provide software engineers and tech-savvy business users with a suite of tools, custom code components, and APIs, enabling them to build and modify applications significantly faster than with full-code development. Low-code is suitable for more complex, business-critical applications, including core system integrations, digital transformation initiatives, and applications requiring greater customization.
Core Overlap: Both low-code and no-code approaches share the overarching goal of accelerating application development, empowering a wider audience to participate in technology creation, and simplifying the process of building digital solutions. The distinction between low-code and no-code is not merely about the required coding skill level, but more profoundly about the strategic scope and complexity of the applications they enable.
No-code empowers tactical, departmental solutions, while low-code supports more complex, business-critical initiatives that require more customization. This implies a tiered and complementary approach to LCNC adoption within an enterprise’s overall digital strategy. For executives, understanding this means they can strategically allocate the right LCNC tool to the right problem, leveraging no-code for rapid, localized problem-solving by business users and low-code for more robust, integrated enterprise solutions, often with professional developer involvement. This approach helps to avoid misapplication and maximizes the value derived from LCNC investments.
How LCNC Platforms Simplify Software and AI Development
A key strength of LCNC platforms is their ability to abstract away the underlying coding languages, complex logic, and syntax. This allows users to concentrate on the application’s functionality and design, rather than getting bogged down in intricate programming details. The result is that non-technical users can build functional software with minimal to no programming knowledge.
These platforms offer intuitive visual app design tools, including drag-and-drop interfaces, visual workflows, and a comprehensive library of pre-built components such as forms, buttons, and data tables. This enables the rapid assembly of functional and aesthetically pleasing applications.
Crucially, enterprise-grade LCNC platforms are increasingly integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) capabilities directly into their offerings. This means users can leverage features like predictive analytics and natural language processing (NLP) without needing specialized AI expertise or writing complex algorithms. The integration of pre-built AI/ML components and AutoML capabilities into LCNC platforms directly addresses the “limited understanding of AI’s capabilities” that often plagues organizations. This is because it makes sophisticated AI functionalities consumable and configurable, rather than requiring deep knowledge of algorithms or data science. Users, including business professionals, do not need to grasp the intricate mathematical models or coding behind AI. Instead, they can focus on what the AI does (e.g., predictive analytics, natural language processing, computer vision) and how to apply it to their specific business problem through visual configuration. This shifts the required skill set from deep technical expertise to domain knowledge and practical problem-solving, making AI far more accessible, less intimidating, and immediately useful for a broader audience within the organization.
For AI-powered applications specifically, LCNC platforms provide a streamlined workflow: users can upload their data, define what they intend to predict or analyze, and configure options like target variables or model types. The platform then automatically handles complex steps such as data preprocessing, algorithm selection, and model training. Once trained, these AI models can be seamlessly deployed to existing business systems via APIs or direct integrations.
The Rise of “Citizen Developers” and Expanded Access
LCNC development fundamentally democratizes software creation, shifting it from an exclusive domain of professional developers to a broader pool of talent within the organization. This empowers business users—the “citizen developers”—to quickly develop solutions tailored to their specific needs without constant reliance on or bottlenecks from the central IT department. This empowerment of citizen developers directly addresses and alleviates the pervasive “IT bottleneck” problem often faced by organizations. A common frustration for executives is the slow pace of digital initiatives due to overstretched IT departments and long development backlogs. By enabling business users without coding experience to create applications and automate processes independently, LCNC bypasses this traditional constraint. This decentralization means that departments can develop and deploy solutions for their specific needs much more quickly, without having to wait for central IT’s availability. This not only accelerates project completion but also fosters a stronger sense of ownership and direct problem-solving among employees, leading to a more agile and responsive organizational structure for digital transformation.
This decentralization fosters a culture of innovation across various departments. For instance, HR teams can independently create employee onboarding systems and marketing teams can build apps for customer surveys, all without extensive IT involvement. Crucially, LCNC bridges the gap between domain expertise and technical implementation. It allows those individuals who are most familiar with specific business challenges to directly experiment with, iterate upon, and deploy AI-powered tools, ensuring that solutions are highly relevant and immediately impactful. The democratization of AI through LCNC fundamentally shifts the innovation bottleneck from scarce and expensive IT resources and specialized AI talent to the business users’ ability to identify and implement solutions. Traditional AI development is notoriously resource-intensive, requiring highly specialized data scientists and software engineers. This scarcity of talent often acts as a significant impediment, slowing down AI adoption and innovation. LCNC platforms explicitly reduce dependency on scarce technical resources and empower non-technical staff to contribute to digital innovation. This means the primary constraint on innovation moves from the supply of expert developers to the internal capacity of business units to identify problems and build solutions. By enabling those closest to the business challenges to create AI-powered tools, organizations can unlock a new wave of distributed innovation, fostering a more agile and responsive enterprise that can adapt more quickly to market changes.
III. LCNC as the Catalyst for AI Adoption and Business Transformation
Accelerated Development and Time-to-Market
LCNC platforms fundamentally act as a “fast-forward button” for application development. They enable businesses to build and deploy applications significantly faster, with reports indicating up to 90% faster deployment compared to traditional methods. Some platforms boast 10x quicker app builds and a 31% reduction in overall project timelines. This rapid development cycle is critically important for maintaining agility in today’s dynamic business environments. It allows organizations to respond swiftly to evolving market demands and capitalize on new opportunities. For AI-powered applications specifically, LCNC platforms drastically reduce the time-to-deployment. While traditional AI projects often require months for development and validation, LCNC platforms enable users to build functional prototypes and deploy solutions in days or weeks.
Cost Efficiency and Resource Optimization
LCNC platforms offer substantial cost savings by minimizing the need for expensive, specialized coding expertise and significantly trimming overall development expenses. Reports indicate that application development costs can drop by up to 70%, and ongoing maintenance expenses can be reduced by as much as 60%. This reduction in dependency on scarce and highly compensated technical talent allows organizations to reallocate valuable resources. The savings generated from workflow automation and reduced development overhead can be strategically reinvested into other activities such as research and development, marketing, or enhanced customer support. For example, a German airport successfully utilized low-code to cut staffing expenses by a remarkable 40%, illustrating tangible financial impact. The combination of accelerated development and lower costs creates a powerful positive feedback loop, enabling more frequent experimentation, rapid prototyping, and faster adaptation to market changes. If the cost and time required for development are drastically reduced, as indicated by “up to 90% faster” and “up to 70% lower development costs”, organizations are no longer constrained by the traditional development bottleneck. This economic and temporal freedom allows companies to “quickly experiment with AI ideas, gather feedback, and iterate on their solutions”. This iterative capability fosters agility, meaning businesses can respond to market demands and competitive threats far more swiftly. This is not just about saving money; it is about enabling a continuous innovation cycle that traditional development often struggles to maintain due to its inherent expense and slowness, translating directly into sustained market leadership.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency and Productivity
LCNC tools are powerful enablers of operational efficiency, streamlining business operations by automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks across a wide array of functions, including HR, finance, operations, and supply chain management. This automation significantly reduces manual errors, enhances accuracy, and improves overall efficiency. AI-driven automation minimizes human intervention in routine processes, freeing employees to focus on more strategic, creative, and higher-value activities. For instance, an e-commerce team can leverage no-code AI to build sophisticated recommendation models for personalized customer experiences, and a café owner reported reducing food waste by 36% in just two months by implementing a simple AI inventory system. The productivity gains are substantial: data suggests that 90% of low-code developers handle fewer than five app requests monthly, indicating increased output from smaller teams. Furthermore, business owners have reported saving 5-15 hours weekly on administrative tasks alone, allowing them to use those hours to focus on customer relationships and strategic growth.
Fostering Innovation and Agility
LCNC platforms play a pivotal role in fostering a culture of pervasive innovation across the enterprise by making application development accessible to individuals without extensive coding experience. This empowers various departments and employees to take ownership of automation and digital initiatives, rather than waiting for central IT. They facilitate rapid prototyping and iteration, enabling organizations to quickly experiment with new AI ideas, gather immediate feedback, and rapidly iterate on solutions. This iterative approach significantly accelerates the time-to-market for new AI applications, providing a crucial competitive edge.
Improved Customer and Employee Experiences
LCNC, particularly when integrated with AI, can deliver a superior customer experience. This includes real-time customer service through conversational AI, intelligent chatbots, and virtual assistants that handle queries, track orders, and make recommendations, improving response times and reducing human workload. It enables personalized customer experiences at scale, leveraging AI for highly targeted product recommendations, curated content feeds, and tailored offerings that enhance engagement and conversion rates. For employees, LCNC AI is a powerful tool for enriching job roles. By automating repetitive, mundane tasks, AI frees up staff to focus on more complex, creative, and ultimately more valuable work, leading to increased job satisfaction, improved well-being, and greater overall productivity.
The numerous and varied measurable ROI examples, such as the 40% reduction in staffing expenses for a German airport, the 36% food waste reduction for a café, the 64% reduction in stockouts for a kitchenware shop, the 25% increase in mobile sales for an e-commerce company, the 509% five-year ROI for Appian customers, and the 10x ROI for EDP Renewables, provide concrete, compelling evidence that LCNC AI is not merely hype but delivers tangible, quantifiable business value. These are not just theoretical gains but proven impacts on operational efficiency, cost reduction, revenue generation, and customer satisfaction across diverse industries and business functions. This concrete evidence demonstrates that LCNC AI can deliver “meaningful value”, shifting the conversation from “if” AI can deliver value to “how much” and “how quickly.”
IV. Addressing Executive Concerns: ROI, Risk, and Workforce Evolution
Quantifying the Return on Investment (ROI)
It is important to acknowledge that measuring the Return on Investment (ROI) for AI initiatives can be complex. Many of AI’s beneficial impacts are indirect, qualitative, and accrue over the long term, making traditional, short-term ROI calculations difficult to apply. Unlike simple software projects, AI often reshapes fundamental workflows, making it more about unlocking new capabilities than just cutting corners.
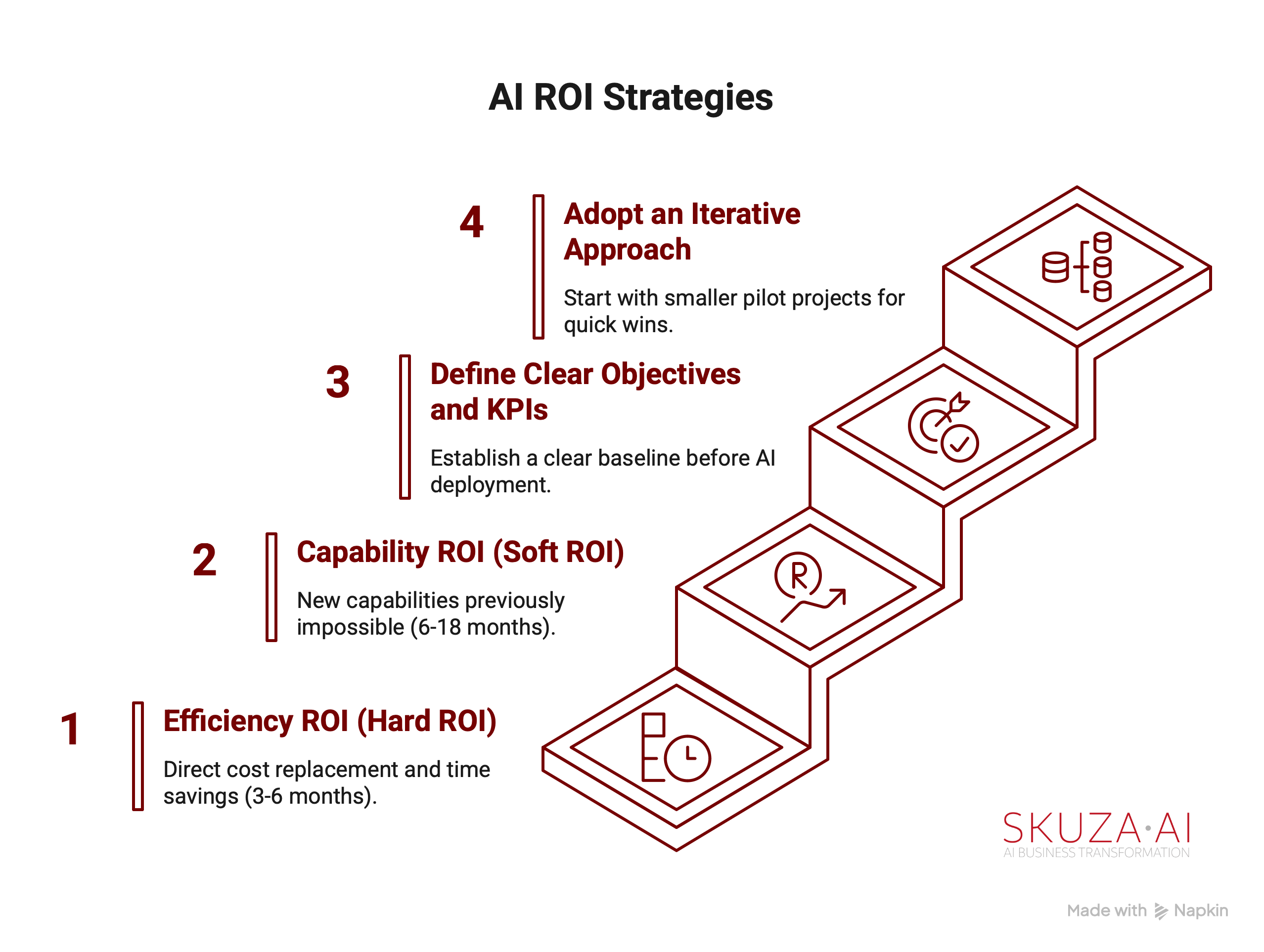
To provide a comprehensive view, executives should adopt a multi-layered approach to measuring AI ROI:
- Start with “Efficiency ROI” (Hard ROI): This focuses on direct, quantifiable cost replacement and time savings, typically realized within 3-6 months. Examples include labor hours saved, error rate reductions, and faster processing times. Specific instances include 40% of support tickets being auto-resolved, a 30% faster pull request cycle time for developers, and a 60% reduction in time spent writing internal documentation. This is the visible, reportable ROI that CFOs often expect.
- Progress to “Capability ROI” (Soft ROI): Beyond immediate efficiencies, AI enables new capabilities that were previously impossible or cost-prohibitive. This layer, typically measurable in the long-term from around 6-18 months, focuses on expanded customer segments, increased net promoter scores (NPS), and intangible gains like higher employee morale, and better strategic alignment. Examples include achieving true 1:1 personalization at scale, a 10x increase in content velocity for faster iteration, and real-time operational intelligence dashboards that were too expensive to build manually before.
- Define Clear Objectives and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Successful AI adoption requires establishing a clear baseline before AI deployment and setting specific, measurable KPIs. These should include metrics like development time, project completion rate, and cost reduction.
- Adopt an Iterative Approach: To mitigate risk and build confidence, it is advisable to start with smaller pilot projects that target quick wins or demonstrable cost savings. This allows for iterative learning and validation of value before scaling enterprise-wide.
LCNC platforms inherently accelerate the realization of ROI by dramatically reducing development time and costs. This speed enables faster experimentation and iteration, allowing organizations to quickly identify and scale high-value use cases. Significantly, data shows that 84% of companies with strict enterprise requirements that are using low-code have a positive ROI.
Mitigating Risks: Security, Governance, and Scalability
C-level executives rightly express concerns about potential risks associated with LCNC and AI, including limited customization, vendor lock-in, performance limitations, and critical issues related to security and data privacy. Addressing these concerns proactively is essential for successful adoption.
- Limited Customization & Flexibility: LCNC platforms, particularly no-code solutions, can be restrictive. They often rely on preconfigured modules and visual templates, which may limit advanced customization, hinder the creation of highly specialized models, or make integration with external libraries difficult. This can lead to model suboptimality if fine-grained control is required.
- Mitigation: Low-code platforms offer greater flexibility, allowing professional developers to access and modify underlying code for complex needs. The future may see hybrid approaches that combine the simplicity of LCNC with the flexibility of traditional development through modular plug-ins. Organizations must carefully evaluate whether these solutions align with their long-term goals of flexibility, performance, and security requirements.
- Vendor Lock-In Risks: A significant concern is that most LCNC platforms are proprietary. This creates a dependency on a single vendor’s infrastructure and licensing terms, making it time-consuming and costly to migrate applications to a different platform. Companies may also face unexpected subscription price increases or disruptions if vendor support diminishes.
- Mitigation: Strategic platform selection should involve a thorough review of licensing terms, a clear understanding of API support for integration, and consideration of platforms that offer greater openness or portability options. Prioritizing flexibility and integrating LCNC systems with open-source tools can help mitigate this risk.
- Performance and Scalability Constraints: Applications developed on LCNC platforms can sometimes struggle to handle high performance and scalability demands, especially under heavy user loads. Vendor-managed infrastructure might introduce latency spikes or throttling if computational demands exceed predefined thresholds.
- Mitigation: Enterprise-grade LCNC AI platforms are designed with scalable infrastructure management, utilizing serverless architectures and container orchestration to automatically adjust resources to meet fluctuating demand, reducing downtime and cost overruns. However, teams requiring extremely strict Service-Level Agreements (SLAs) for real-time inference may find built-in autoscaling policies less granular. Leveraging advanced network solutions, scalable architectures, and optimized hosting environments can help maintain enterprise-grade performance.
- Security and Data Privacy Concerns: The abstraction provided by LCNC platforms, while simplifying development, can inadvertently obscure critical security controls and introduce privacy risks. Over 70% of AI data breaches come from pipeline misconfigurations, and 55% of platforms may lack end-to-end encryption, making sensitive information vulnerable. Default connector settings frequently grant broad data permissions, giving non-technical users the chance to ingest or expose personally identifiable information (PII) without even realizing the implications, bypassing established IT governance. Organizations relying solely on platform defaults experience 30% more audit failures than those enforcing manual review processes.
- Mitigation: Robust data governance is paramount. This includes defining clear data governance objectives, building a dedicated data governance team with compliance and legal experts, implementing strict data quality controls, and locking down data security with encryption and access controls. Role-based access controls (RBAC), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and audit logs are crucial for tracking data access and preventing unauthorized usage. It is also vital to implement data retention and deletion policies to manage data lifecycle and comply with regulations like GDPR and CCPA. Enterprise-grade LCNC platforms should have built-in security features, but IT professionals must control access to data assets and be alerted to permissions that may need stricter control. Requiring developers to use a platform’s sandbox can limit access to resources and restrict data sharing capabilities, encouraging transparency.
- Shadow IT: The ease of creating applications without IT oversight that can lead to a lack of standardization, exposure to potential security vulnerabilities, and integration challenges.
- Mitigation: Establishing clear governance models for citizen developers, defining roles and responsibilities, and providing training on best practices, security, and compliance can help manage this risk. Creating a Center of Excellence (CoE) for LCNC can establish best practices, provide support, and ensure security and compliance standards are maintained.
Workforce Evolution: Augmentation, Not Displacement
The concern that AI will lead to widespread job displacement is a significant barrier to adoption for many executives and their workforce. However, the prevailing perspective among experts and early adopters is that AI, particularly when integrated through LCNC platforms, primarily augments human capabilities rather than replacing them entirely.
- Job Augmentation: AI is designed to support employees, helping them perform their jobs faster, better, and with more creativity. By automating repetitive, mundane tasks, AI frees up employees to focus on more complex, strategic, and higher-value work, enriching their jobs instead of eliminating them. For example, AI can draft the bulk of a report in minutes, allowing a human to refine and add creative insights. This shift not only makes the work environment more exciting but also boosts job satisfaction and well-being.
- Creation of New Roles and Opportunities: Companies that have successfully integrated AI often created new roles and opportunities for their workforce. This includes roles focused on AI governance, ethics, and specialized integration. The demand for “no-code architects” is projected to rise by 40%, and traditional developers are expected to shift towards specialized AI integration roles.
- Reskilling and Upskilling: To harness AI’s full potential, organizations must invest in reskilling and upskilling their existing workforce. This includes training employees on how to effectively use LCNC platforms and AI tools, fostering AI literacy across all levels of the organization. Proactive change management and open communication are key to addressing fears and highlighting how AI will augment roles, making employees part of the AI journey rather than perceiving themselves as victims.
- Bridging the Skills Gap: LCNC platforms lower skill barriers, helping more people acquire proficiency in various fields. This democratization of development allows non-technical users and citizen developers to create and deploy AI-driven applications with minimal programming knowledge, effectively bridging the talent gap in AI development.
V. The Future Landscape: Convergence and Continuous Evolution
The convergence of AI with low-code and no-code platforms is not a fleeting trend but a fundamental reshaping of the software development landscape. This fusion is creating a new era where machine learning enhances development speed compared to traditional methods, AI assists in decision-making processes, and LCNC tools democratize technology creation.
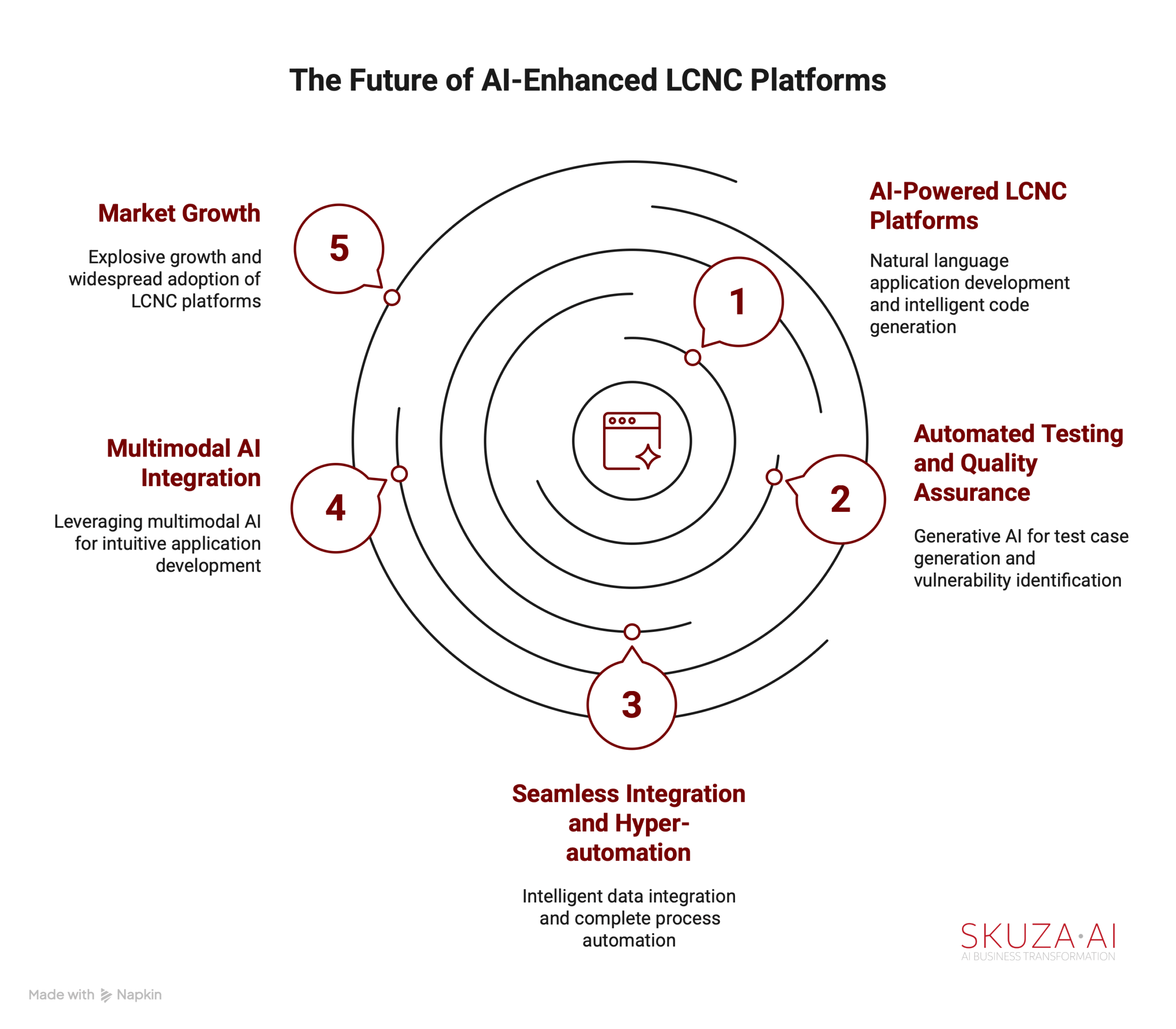
- AI-Powered LCNC Platforms: The future will see increasingly sophisticated AI features embedded within LCNC platforms. This includes natural language application development, where users can describe their needs in everyday language, and AI will automatically generate the application structure, data models, and workflows. Intelligent code generation and completion will become more prevalent, with AI auto-creating functions and modules based on comments or requirements.
- Automated Testing and Quality Assurance: Generative AI will revolutionize testing by automatically generating comprehensive test cases and synthetic test data, proactively identifying vulnerabilities, and even self-healing code. This will drastically reduce quality assurance time and improve application quality and security.
- Seamless Integration and Hyper-automation: Future platforms will offer more intelligent data integration and management, automatically mapping and transforming disparate data sources. The trend towards hyper-automation will see businesses using AI for complete process automation, reducing human involvement and boosting operational efficiency across complex workflows.
- Multimodal AI Integration: Future LCNC platforms will enable more intuitive application development experiences by leveraging multimodal AI that can understand and process text, images, voice, and video inputs. This seamless integration with emerging technologies like IoT, blockchain, and augmented reality (AR) will enable businesses to create innovative solutions across diverse sectors.
- Market Growth: The LCNC market is projected for explosive growth, with market experts predicting it will reach $187 billion by 2030. Research highlights that by 2025, 75% of large enterprises will use at least four low-code development tools, and that 65% of application development will be achieved through no-code AI platforms. This signifies a widespread adoption and integration of LCNC into core business operations.
Organizations that track AI and LCNC development trends will be better equipped to navigate the changing technological landscape and achieve innovation and operational efficiency.
Conclusion
The pervasive skepticism among C-level executives regarding AI, largely fueled by high project failure rates and common misconceptions, presents a significant barrier to realizing its transformative potential. However, low-code and no-code platforms offer a compelling and pragmatic solution to bridge this AI divide.
LCNC democratizes AI development by abstracting away technical complexities, empowering business users—the “citizen developers”—to create AI-powered applications without extensive coding knowledge. This shifts the innovation bottleneck from scarce IT resources to the agility and problem-solving capabilities of the business units themselves, fostering a distributed and responsive innovation model. The integration of pre-built AI/ML components and AutoML within LCNC platforms makes sophisticated AI functionalities accessible and configurable, directly addressing the perception that AI is too complex or only for specialists.
The benefits are quantifiable and compelling: LCNC significantly accelerates development cycles, reduces costs, enhances operational efficiency, and fosters a culture of continuous innovation. Real-world examples demonstrate substantial ROI, from significant cost reductions and productivity gains to improved customer experiences and new revenue streams. This evidence directly counters concerns about AI’s return on investment.
While LCNC platforms come with their own set of considerations, such as limited customization, vendor lock-in, and scalability concerns, these can be effectively mitigated through strategic platform selection, robust data governance frameworks, and a balanced approach that combines citizen development with IT oversight. Furthermore, the fear of job displacement is largely addressed by the reality of AI augmentation, where LCNC tools free employees from mundane tasks, enabling them to focus on higher-value, creative work and fostering new roles within the organization.
The future landscape points towards an even deeper convergence of AI and LCNC, with generative AI capabilities further streamlining development, automating testing, and enabling hyper-automation. For executives, embracing LCNC AI is not merely an option but a strategic imperative. It represents a pathway to unlock enterprise-wide innovation, optimize operations, and secure sustainable growth in an increasingly AI-driven competitive environment. By understanding and strategically leveraging LCNC, organizations can move beyond skepticism to realize the tangible, transformative power of AI.
Based on references:
- Why 85% of AI Projects Fail – Leading the charge on AI | Plan b, accessed September 15, 2025, https://myplanb.ai/why-85-of-ai-projects-fail/
- Common Misconceptions About AI in the Executive Suite – ExCom.ai, accessed September 15, 2025, https://excom.ai/blog/common-misconceptions-about-ai-in-the-executive-suite?ref=blog.superhuman.com
- The State of AI: Global survey | McKinsey, accessed September 15, 2025, https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/quantumblack/our-insights/the-state-of-ai
- Why AI and GenAI Projects Fail: An Executive Leadership Perspective – Medium, accessed September 15, 2025, https://medium.com/@adnanmasood/why-ai-and-genai-projects-fail-an-executive-leadership-perspective-be84216c0463
- The 3 BIGGEST Misconceptions About AI (Debunked by Founders) – Generative, accessed September 15, 2025, https://generativegroup.ai/insights/The-Biggest-Misconceptions-About-AI/
- Generative AI Use Cases and Resources – AWS, accessed September 15, 2025, https://aws.amazon.com/ai/generative-ai/use-cases/
- AI Examples & Business Use Cases – IBM, accessed September 15, 2025, https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/artificial-intelligence-business-use-cases
- Will your job survive AI? – Harvard Gazette, accessed September 15, 2025, https://news.harvard.edu/gazette/story/2025/07/will-your-job-survive-ai/
- AI-powered success—with more than 1,000 stories of customer transformation and innovation | The Microsoft Cloud Blog, accessed September 15, 2025, https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-cloud/blog/2025/07/24/ai-powered-success-with-1000-stories-of-customer-transformation-and-innovation/
- What Is No Code? | IBM, accessed September 15, 2025, https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/no-code
- What Is No-Code Artificial Intelligence (AI)? – Ramp, accessed September 15, 2025, https://ramp.com/blog/what-is-no-code-artificial-intelligence
- (PDF) Low-Code and No-Code Platforms: Democratizing AI Development – ResearchGate, accessed September 15, 2025, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/390742943_Low-Code_and_No-Code_Platforms_Democratizing_AI_Development
- Democratizing AI: Exploring the Impact of Low/No-Code AI Development Tools – Unite.AI, accessed September 15, 2025, https://www.unite.ai/democratizing-ai-exploring-the-impact-of-low-no-code-ai-development-tools/
- AI & Low-Code/No-Code Tools: Predicting the Trends of 2025 – Bubble Developer, accessed September 15, 2025, https://www.bubbleiodeveloper.com/blogs/ai-and-low-code-no-code-tools-predicting-the-trends-of-2025/
- No-Code AI Automation: How Small Businesses Can Transform on a Budget – Medium, accessed September 15, 2025, https://medium.com/@raymond_44620/no-code-ai-automation-how-small-businesses-can-transform-on-a-budget-c40a82441420
- How Low-Code/No-Code is Transforming Business Automation …, accessed September 15, 2025, https://www.ivoyant.com/blogs/how-low-code-no-code-development-is-revolutionizing-business-automation
- How to maximize ROI on AI in 2025 – IBM, accessed September 15, 2025, https://www.ibm.com/think/insights/ai-roi
- Top 7 Low-Code Benefits and Why They’re Important – Appian, accessed September 15, 2025, https://appian.com/learn/topics/low-code/low-code-benefits
- What is Low-Code Governance | Microsoft Power Apps, accessed September 15, 2025, https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/power-platform/products/power-apps/topics/low-code-no-code/what-is-low-code-governance-and-why-it-is-necessary
- AI – No-Code/Low-Code Platform – Ethical Intelligent Technologies, accessed September 15, 2025, https://ethicalintelligent.com/ai-no-code-low-code-platform
- AI Data Governance Best Practices for Security and Quality | PMI Blog, accessed September 15, 2025, https://www.pmi.org/blog/ai-data-governance-best-practices
- Low-code vs. no-code: Key differences and benefits | Zapier, accessed September 15, 2025, https://zapier.com/blog/low-code-vs-no-code/
- ramp.com, accessed September 15, 2025, https://ramp.com/blog/what-is-no-code-artificial-intelligence#:~:text=No%2Dcode%20artificial%20intelligence%20(AI)%20platforms%20allow%20users%20to,%2C%20and%20pre%2Dbuilt%20templates.
- www.techtarget.com, accessed September 15, 2025, https://www.techtarget.com/searchsoftwarequality/definition/low-code-no-code-development-platform#:~:text=No%20code%20is%20typically%20used,integrations%20and%20digital%20transformation%20initiatives.
- What is Low Code? Definition of Visual Development Platform – AWS, accessed September 15, 2025, https://aws.amazon.com/what-is/low-code/
- Risks and Limitations of Low-Code Systems | Singleclic, accessed September 15, 2025, https://singleclic.com/risks-and-limitations-of-low-code-systems/
- aws.amazon.com, accessed September 15, 2025, https://aws.amazon.com/what-is/low-code/#:~:text=Low%20code%20platforms%20provide%20users,processes%2C%20and%20several%20payroll%20functions.
- The Future of Intelligent Automation: How Low-Code/No-Code Platforms are Transforming AI Decisioning – ResearchGate, accessed September 15, 2025, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/389253989_The_Future_of_Intelligent_Automation_How_Low-CodeNo-Code_Platforms_are_Transforming_AI_Decisioning
- The Impact of Generative AI on Low Code – GeneXus Consulting, accessed September 15, 2025, https://www.genexusconsulting.com/en/insights/ai-and-low-code/
- 20 Pros & Cons of Low Code / No Code AI Development [2025 …, accessed September 15, 2025, https://digitaldefynd.com/IQ/pros-cons-of-low-code-no-code-ai-development/
- Low-Code ROI: Measuring Business Value and Cost Savings – Deployd, accessed September 15, 2025, https://deployd.co/blog/low-code-roi-measuring-business-value-and-cost-savings
- Real-World Applications of No-Code AI in Business Operations – ResearchGate, accessed September 15, 2025, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/392521495_Real-World_Applications_of_No-Code_AI_in_Business_Operations
- Empowering Small Businesses: How No-Code AI Tools Drive Scalable Growth | by WebClues Infotech | Jun, 2025 | Artificial Intelligence in Plain English – Medium, accessed September 15, 2025, https://medium.com/ai-in-plain-english/empowering-small-businesses-how-no-code-ai-tools-drive-scalable-growth-513fdeb82466
- Case Studies | appian.com, accessed September 15, 2025, https://engage.appian.com/mining/case-studies
- You’re Measuring AI ROI All Wrong. Here’s What Actually Matters | by John Munn – Medium, accessed September 15, 2025, https://medium.com/@johnmunn/youre-measuring-ai-roi-all-wrong-here-s-what-actually-matters-4158432e7e0b
- High-Impact AI for the Boardroom — Steering the Enterprise Toward Sustained ROI | by Adnan Masood, PhD. | Medium, accessed September 15, 2025, https://medium.com/@adnanmasood/high-impact-ai-for-the-boardroom-steering-the-enterprise-toward-sustained-roi-7ead26cefdf6
- AI’s Business Value: Lessons from Enterprise Success | Google Cloud Blog, accessed September 15, 2025, https://cloud.google.com/transform/ais-business-value-lessons-from-enterprise-success-research-survey
- How Generative AI is Changing the Future of Low-Code Platforms, accessed September 15, 2025, https://www.kovaion.com/blog/how-generative-ai-is-changing-the-future-of-low-code-platforms/
- AI in the workplace: A report for 2025 – McKinsey, accessed September 15, 2025, https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/superagency-in-the-workplace-empowering-people-to-unlock-ais-full-potential-at-work

